








What if you could predict delays before they even happen? Not after a deadline slips or a client chases an update, but before your team even realizes there is a risk. Imagine knowing exactly which tasks could push your project off track and stopping the problem before it even begins. Sounds like a game changer, doesn't it?
In many projects, delays aren’t caused by a lack of effort. They usually start with a single overlooked task that leads to missed deadlines. But what if you had a way to spot them early and plan accordingly? That's where the Critical Path Method in Project Management comes as a savior for many. In this blog, you’ll learn what CPM is, how it works, its importance, and how to build one alongside tools like PERT and Gantt charts. Let's dive in!
Table of Contents
1) What is the Critical Path Method (CPM)?
2) Why Use Critical Path Analysis?
3) How to Find a Project's Critical Path?
4) Benefits of the Critical Path Method
5) Limitations of Critical Path Method
6) Critical Path Method vs PERT vs Gantt Charts
7) Conclusion
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project scheduling technique that helps find the sequence of dependent tasks that directly impact the project’s completion time. This sequence is known as the Critical Path. Any delay in these tasks will cause a delay in the overall project.
CPM helps you see which tasks must be done in a certain order and how long each one will take. It also tells you which tasks cannot be delayed (these are on the Critical Path) and which can have extra time (these are not as urgent).
CPM helps you understand how your project flows and where your attention is needed most. Here are some key reasons to use Critical Path Method in Project Management:
1) Improves Planning: Compares your plan with real progress, so future projects can be planned more accurately.
2) Manages Resources Better: Prioritizes critical tasks, helping avoid resource shortages and overload.
3) Avoids Bottlenecks: Shows which tasks depend on others, so you can schedule work to prevent delays.
4) Shows Task Order: Makes it easy to see what needs to happen first and what comes next.
5) Informs Scheduling: It is particularly useful when managing projects with tight deadlines or limited resources.
6) Supports Smart Decisions: Helps you focus on the tasks that matter most for finishing on time.
7) Reduces Risk: Identifies problem areas before they cause delays, so you can fix them quickly.
Identifying the Critical Path is a structured process that involves some essential steps. Here's how to do it:
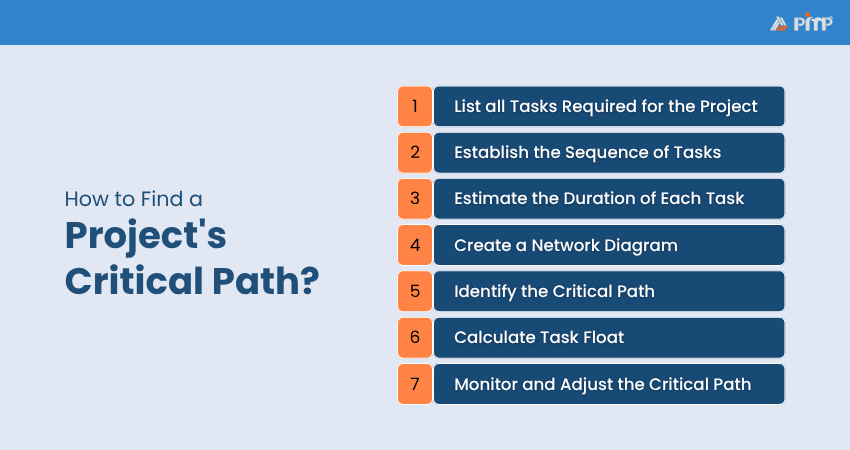
Start by dividing the project into individual tasks. Later, you need to write down every task needed to finish the project. This can be done using a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) or a task list. Each task should be small and clear, with a specific goal.
Next, you need to find the order in which the tasks should happen. Some tasks can be done at the same time, while others need to wait until previous ones are finished. This step is about spotting dependencies. Understanding this helps you build a solid project timeline.
For example:
1) Task D can’t start until Task A is finished
2) Tasks A and B might run at the same time
3) Task E may depend on D, and Task F might follow E
Now, you need to fix a time for how long a task will take to complete from start to finish. It is important to be realistic and, if needed, include buffer time for possible delays. To plan accurately, you can use these two techniques:
1) Forward Pass: Start from the beginning of the project and move forward. This helps calculate the earliest start and finish times for each task.
2) Backward Pass: Work backward from the end of the project to find the latest start and finish times.
These two calculations help you identify which tasks are critical and how much flexibility others have.
A network diagram, also known as a project logic diagram, is a visual map of the sequence of tasks and their dependencies. Each task is shown as a box (node), and arrows between them show dependencies. There are two common types of diagrams:
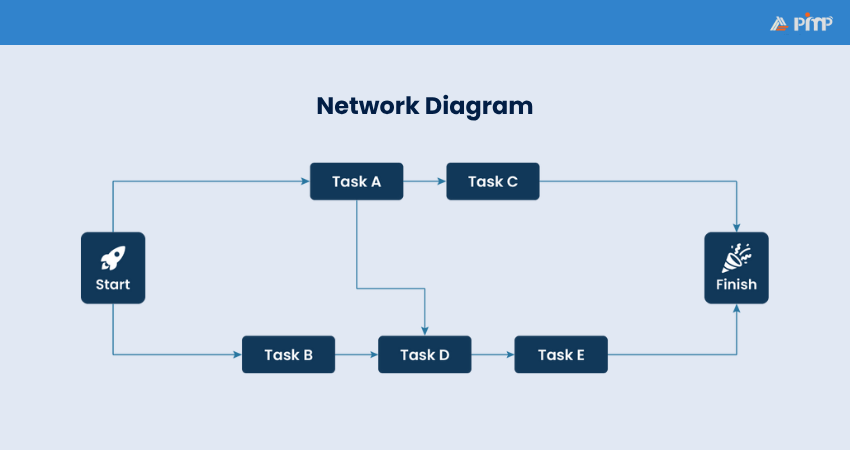
1) Activity-on-Node (AON): Tasks are represented as nodes.
2) Activity-on-Arrow (AOA): Tasks are represented on the arrows, with events as nodes.
Advance to the next level of leadership with our Program Management Professional (PgMP)® Certification – Register today!
Now that your network is set up, it is time to find the Critical Path, which is the longest sequence of dependent tasks from the start to the end of the project. These are the tasks that:
1) Must be completed on time
2) Have no float (flexibility)
3) Directly affects your project’s finish date
For example, if Tasks A → D → E → F take 10 days and that is the longest route through your project, then that will be your Critical Path.
Float, also called slack, is the amount of time a task can be delayed without affecting the end date of the project. Tasks on the Critical Path have zero float, meaning they can’t be delayed at all. But tasks not on the Critical Path might have some flexibility.
1) Total Float: How much a task can be delayed without delaying the whole project.
2) Free Float: How much a task can be delayed by not delaying the start of the next task.
Once the project starts, keep a close eye on the Critical Path. If any tasks are delayed, the entire project could be at risk. Using tools or software like Microsoft Project can make tracking easier. They help update your schedule, calculate float automatically, and keep the project moving smoothly. Meanwhile, you can:
1) Update the timeline regularly
2) Check task progress
3) Recalculate the Critical Path if anything changes
Here are some of the benefits of using Critical Path Method in Project Management:
Once you know which tasks are on the Critical Path, you know which ones are most important. This helps you focus on what really matters, the tasks that must be finished on time to keep the project moving. Even if other small tasks are delayed, these key tasks stay on track. It helps:
1) Focus on tasks that directly affect project deadlines
2) Lead quick decisions during delays or issues
3) Ensure efficient use of resources on high-priority tasks
If you use CPM with Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) charts, you can build a more realistic schedule. PERT helps you guess task durations more carefully by looking at best-case, worst-case, and average time estimates. This helps you:
1) Plan better
2) Spot risky tasks early
3) Avoid last-minute delays
When you combine CPM with a Gantt chart, you get a simple timeline view of your project. These visuals are great for team members and clients who prefer to see the schedule visually. It is helpful during project reviews or when presenting updates to stakeholders. It shows:
1) When tasks start and end
2) Which tasks can happen at the same time
3) What needs to be done next
CPM shows everyone what tasks need to be done and when. This makes it easier for everyone on the team to stay on the same page, from team members to stakeholders, managers, and clients. It aims to:
1) Improve clarity around responsibilities and deadlines
2) Reduce confusion and miscommunication
3) Keep stakeholders informed and engaged
Gain real-world Project Management knowledge with our PMI Project Management Ready® Certification – Join now!
While the Critical Path Method in Project Management is useful for planning, it has some limitations. Those include:
1) Needs Accurate Data: If task times or dependencies are wrong, then the Critical Path and your schedule will be unreliable.
2) Not Very Flexible: In fast-moving or Agile projects, CPM can be too rigid and slow to update.
3) Overlooks Non-critical Tasks: It focuses on critical tasks, but ignoring smaller tasks can still cause quality or team issues.
4) Doesn’t Track Resources: CPM doesn’t show if people are overbooked or working on multiple tasks at once, which can cause delays.
CPM works best with stable, well-planned projects and should be combined with tools that handle changes and resource planning better.
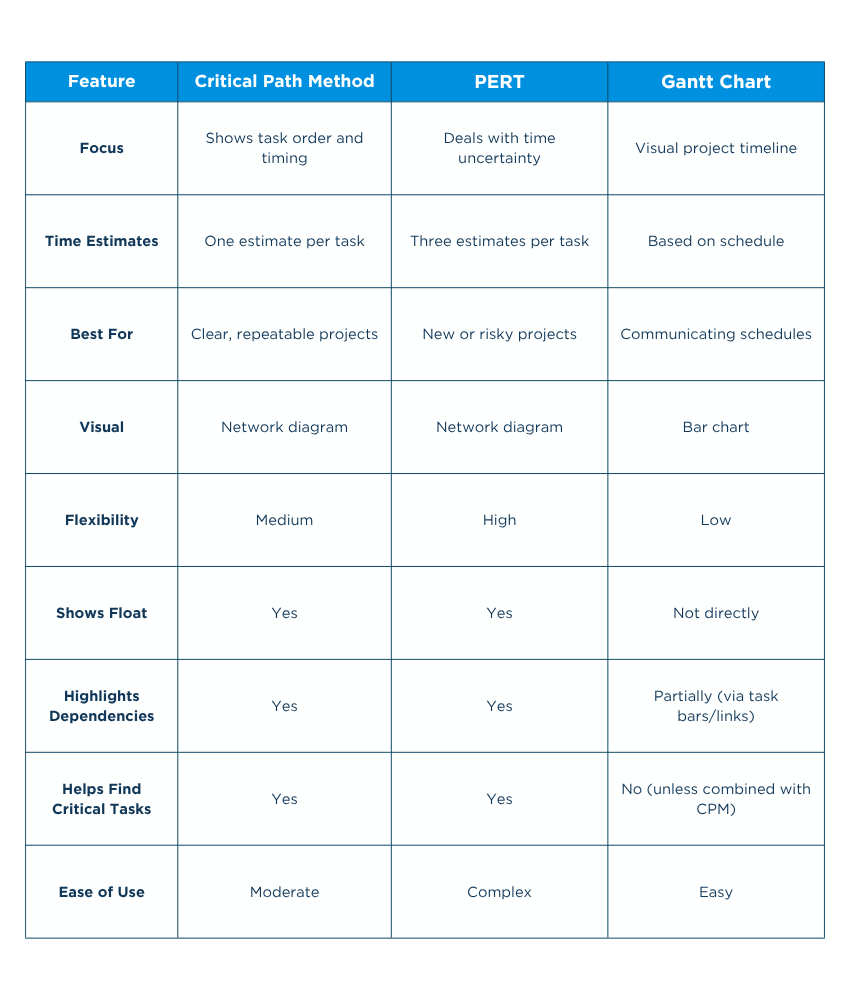
Here’s a simple comparison of the Critical Path Method vs PERT vs Gantt Charts:
The Critical Path Method in Project Management is one of the most effective tools for planning, scheduling, and staying on track. By focusing on this path, you can stay in control and deal with problems before they cause major delays. If you want your project to finish on time and with fewer surprises, understanding and applying CPM is a smart move.
Boost your Project Management career with our Project Management Institute (PMI)® Certification – Lead with confidence and success!






© Copyright 2025. All rights reserved. Contact: PMP® TRAINING ACADEMY.


