







 10 Sep 2024
10 Sep 2024

 12 Sep 2024
12 Sep 2024



Have you ever started a project with high expectations, only to feel overwhelmed as tasks pile up and priorities shift? You are not alone. One of the important reasons why Projects do struggle is due to a lack of clear structure. This is where Project Management Phases play an integral role in helping teams move forward with clarity, confidence, and control.
As you move into another year, work environments are changing rapidly and getting more dynamic. This means managing projects requires an organized structure for ensuring successful completion. In this blog, you will learn about the Project Management Phases, their key steps and the benefits that will keep your goals clear, risks in check and everyone aligned.
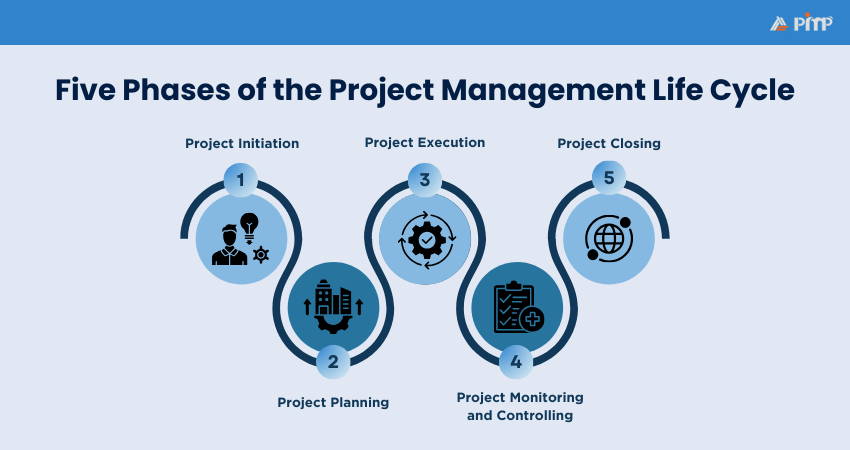
Project Management Phases are the key segments of a project that guides a project from start to finish in a structured way. They help Project Managers plan effectively, allocate resources wisely, and keep teams in alignment with project goals. By breaking projects into phases, complex tasks become simpler to manage and control. According to the Project Management Institute (PMI), there are five key Project Management Phases:
a) Project Initiation
b) Project Planning
c) Project Execution
d) Project Monitoring and Control
e) Project Closure
A Project Management Lifecycle provides a structured framework to guide projects to successful completion. It is made up of five phases that help Project Managers and teams to plan effectively, execute tasks properly, and deliver outcomes in alignment with organizational goals. Let’s look at each phase in more detail.
In this stage, a project is formally authorized, and its feasibility is evaluated. Here, Project Managers and stakeholders define the project’s purpose, scope, and benefits. It makes sure everyone involved has a shared understanding of the project’s aims and why it is important.
In this phase, it is determined whether the project is valuable to pursue or not. Factors, such as potential risks, resources, costs, timelines, and alignment with organizational strategy, are assessed. A well-executed initiation reduces uncertainty and sets up a strong foundation.
a) Project Sponsor: Sets the strategic direction, secures funding, and provides formal approval to start projects.
b) Project Manager: Develops the project charter, identifies stakeholders and conducts initial risk and feasibility assessments.
c) Stakeholders: Contribute insight into business requirements, criteria for success and potential constraints.
d) Business Analysts: Supports required identification, governance and alignment with the organizational standards.
e) Project Management Office PMO: Provides templates, best practices and guidance on feasibility assessments, risk and stakeholder engagement.
The planning phase turns the project’s vision into an executable plan. Project Managers define the project scope, deliverables, timelines, budgets, communication channels and Risk Management strategies. This phase outlines how the project will be executed and monitored.
Strong planning helps teams to anticipate challenges, allocate resources properly, and set realistic expectations. It ensures everyone understands how their roles and responsibilities contribute to project goals. This acts as a point of reference throughout the project lifecycle, eliminating confusion and improving control.
a) Project Manager: Leads the planning activity and combines all planning components into a centralized project plan.
b) Project Sponsor: Reviews and approves the plan formally. This supports escalation and decisions for resource allocation.
c) Project Team Members: Provide task estimates, identify dependencies, and emphasize potential risks.
d) Subject Matter Experts: Provide technical and domain expertise to polish the scope and ensure project feasibility.
e) PMO: Provides templates, governance guidance, and ensures alignment with overall organization policies.
The execution phase is where the project work takes place. Here, teams begin completing tasks, developing deliverables, and collaborating to meet project objectives. For keeping the work progressing as planned, this phase requires strong leadership, communication and collaboration.
The focus of this phase is on managing people, processes, and resources efficiently. Project Managers monitor daily activities, resolve issues, manage stakeholder expectations and ensure quality standards are met. A successful execution results in tangible outputs that steer projects closer to successful completion.
a) Project Manager: Monitors day-to-day operations, manages risks, and ensures work is in alignment with the project plan.
b) Project Team Members: Execute the assigned tasks, report on progress, and collaborate with other departments to deliver outcomes.
c) Stakeholders: Reviews the progress, provides essential feedback, and supports important decisions.
d) Vendors or Contractors: Deliver specialized services or materials as per the contractual agreements.
e) PMO: Ensures execution is followed by approved methodologies and governance standards.

The monitoring and controlling phases run in parallel with execution to make sure projects are on track. Here, the Project Manager tracks the performance by utilizing key metrics for scope, schedule, cost, and quality. In case of any deviations from the plan, they are identified proactively, and corrective measures are taken immediately.
This phase is essential to prevent small issues from escalating into major problems. Through continuous monitoring, it supports informed decision-making, effective Risk Management and alignment with stakeholder expectations. This makes sure the project delivers value while staying within the agreed constraints.
a) Project Manager: Analyses performance data, manages transition and implements corrective actions when needed.
b) Project Sponsor: Reviews reports, approves major changes formally and provides strategic guidance.
c) Project Team Members: Reports progress, highlights issues and supports corrective actions for maintaining project value.
d) Quality Assurance Teams: Ensure deliverables meet the required organizational standards and compliance needs.
e) PMO: Provides valuable insight, supports reporting and makes sure governance compliance is maintained.
The closure phase formally marks the end of the project. In this stage, deliverables are completed and handed over, contracts are closed, documentation is finalized and project resources are released. Also, stakeholders confirm that objectives are met, and the project outcomes are acceptable.
This stage also focuses on learning and improving aspects. For this, teams review what went well, what challenges occurred and how future projects can benefit from this insight. Through proper closure. The project ends in a controlled and professional manner, rather than simply putting an end to it.
a) Project Manager: Confirms acceptance of deliverables, completes documentation and leads sessions on lessons learned.
b) Project Sponsor: Approves the final outcomes and signs off formally on the project completion.
c) Stakeholders: Responsible for validating results and providing final feedback.
d) Project Team Members: Supports knowledge transfer and completes any remaining tasks.
e) PMO: Ensures the closure procedures are followed and stores project records for future reference.
Build strong Project Management fundamentals with Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) ® Training – Join today!
Effective use of Project Management Phases optimizes processes in various ways. Let's look at its advantages: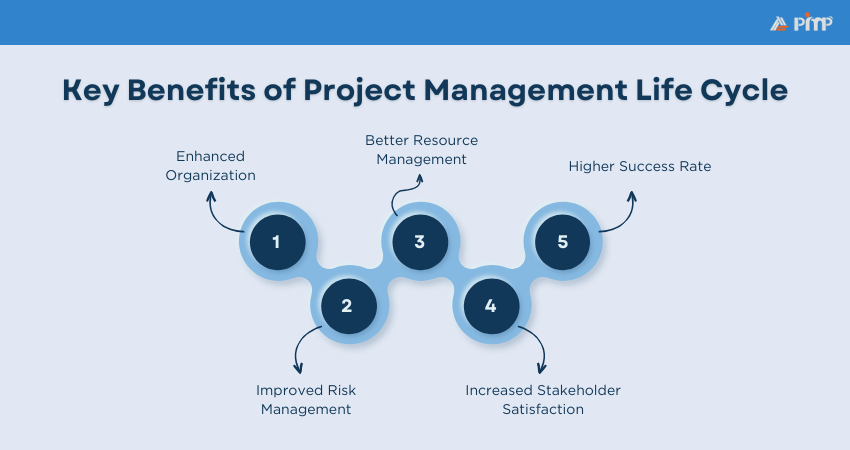
a) Enhanced Organization: By following a structured approach, you can ensure that all project activities are well-organized and aligned with the project goals. This further results in a more cohesive and efficient workflow.
b) Improved Risk Management: Each phase includes risk assessment and mitigation strategies, thus helping to identify potential issues early and address them proactively. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions and keeps the project on track.
c) Better Resource Management: Efficient allocation and utilization of resources are ensured, reducing waste and optimizing productivity. This ensures that resources are used effectively, maximizing their value.
d) Increased Stakeholder Satisfaction: Regular updates and involvement of stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle help in managing expectations and making sure that their needs are met. This continuous engagement fosters trust and collaboration.
e) Higher Success Rate: A clear roadmap with defined phases increases the likelihood of project success by providing a systematic approach to achieving project objectives. This structured methodology enhances the overall quality and delivery of the project.
Project Management Phases gives you a clear roadmap for turning ideas into successful outcomes. From defining goals to reviewing results, each phase plays an important role in keeping projects organized, controlled, and aligned with business objectives. Following these phases helps teams manage risk, adapt to change and deliver real value, ensuring consistent project success.
Advance your Project Management career with Project Management Institute (PMI)® Certification today!






© Copyright 2025. All rights reserved. Contact: PMP® TRAINING ACADEMY.


