







 10 Sep 2024
10 Sep 2024



Have you ever worked on a project where deadlines kept slipping, budgets went overboard, and everyone seemed busy, but progress was slow? That feeling of frustration usually comes from wasted time, unclear priorities, and complicated processes. Lean Project Management helps fix this by focusing only on what matters most and cutting out the rest.
In this blog, we’ll cover what Lean Project Management is, its five core principles, when to use it, key Lean tools, and the main benefits and challenges. By the end, you’ll see how Lean makes projects simpler, smoother, and less stressful. Let's get started!
Lean Project Management is focused on maximizing customer value while minimizing waste and inefficiencies in project workflows. Rooted in Lean thinking (originally from manufacturing), it emphasizes continuous improvement, eliminating non-value-adding activities, and optimizing resource use.
It uses tools like value stream mapping, pull systems, and just-in-time principles to ensure that every task contributes meaningfully. The aim is faster delivery, better quality, and more satisfied customers.
Lean Project Management follows five key principles that focus on customer value, cutting waste, and encouraging continuous improvement. Let’s explore them one by one.
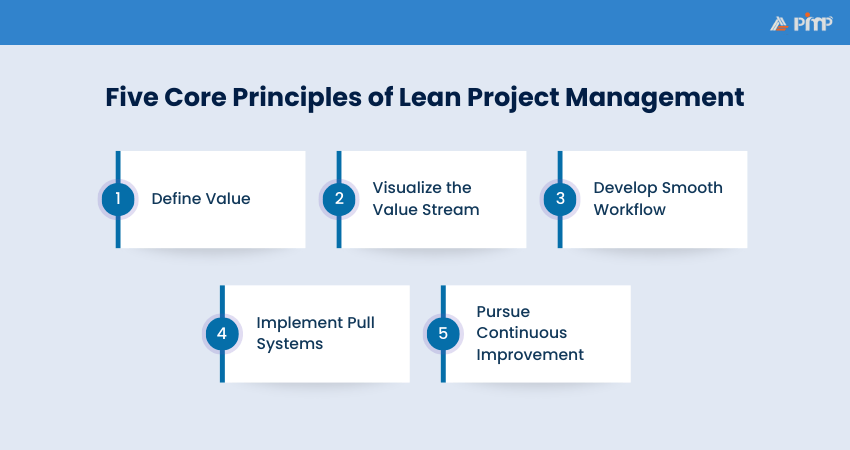
The first step is to understand what the customer truly values. A project is only successful if it meets customer needs, so defining value from their perspective helps set the right priorities. Once the value is clear, it’s easier to decide what to focus on and what to avoid.
Example: Imagine building a mobile app. If customers care most about speed and ease of use, then adding fancy but slow features is a waste. The focus should be on creating a fast, simple app.
After defining value, the next step is to schedule the value stream, the series of steps required to deliver that value. By laying out the entire process, you can spot tasks that don’t add value, like delays or duplicate work. Identifying these wastes sets the stage for smoother workflows.
Example: In a construction project, mapping the value stream might reveal that approvals take too long because paperwork goes through three different offices. By streamlining that process, work can move much faster.
Lead Agile teams with confidence and clarity with our PMI-ACP® Certification – Join today!
With waste reduced, it’s important to ensure workflows without blockages. A smooth workflow keeps tasks moving steadily from one stage to another, avoiding the stop-and-go effect that slows projects down. Once flow is established, the next step is to control how work enters the system.
Example: In a restaurant kitchen, dishes pile up if one chef is overloaded while others wait. By balancing tasks across the team, meals can be prepared smoothly without delays.
Rather than pushing tasks onto teams, a pull system allows teams to take on work only when they have the capacity. This prevents overload and ensures work is done at the right pace. With pull systems in place, teams can focus on doing quality work while continuously improving their approach.
Example: In Software Development, instead of assigning all tasks at once, teams use a Kanban board. New tasks are only “pulled” when a developer finishes their current work, preventing overwhelm.
The final principle is always seeking ways to do better. Continuous improvement encourages teams to review their processes regularly, learn from mistakes, and make small changes that lead to big gains over time. This creates a culture where efficiency and quality are always moving forward.
Example: A retail store asks staff for feedback every week. One small idea, like reorganizing shelves to cut customer wait times, leads to faster service and happier shoppers.
Lean Project Management is most effective when organisations experience frequent delays, rising costs, or inefficiencies that reduce value delivery. It helps eliminate waste, simplify workflows, and ensure resources are used efficiently. This makes it especially valuable in industries where quality, speed, and collaboration are critical.

Manufacturing is where Lean principles first took shape, and they remain highly effective today. It is best applied when production faces bottlenecks, excessive inventory, or inconsistent quality. Using Value Stream Mapping (VSM), Just-in-Time (JIT) delivery, and workplace organization, manufacturers can cut waste, boost efficiency, and deliver quality products faster.
'Construction projects often involve complex coordination between multiple teams, which can lead to delays, rework, and budget overruns. Lean is useful here for improving planning, removing unnecessary steps, and strengthening collaboration. The Last Planner System improves scheduling, cuts material waste, and streamlines workflows for faster, more cost-effective project delivery.
In software and Product Development, customer needs can change rapidly, and speed to market is essential. Lean principles are most effective when teams face long cycle times or frequent changes in requirements. Kanban boards and pull systems help teams balance workloads, speed up releases, and adapt to feedback, ensuring higher quality and customer satisfaction.
Accelerate your career with focused, practical training with our Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) ® Training – Join now!
Lean Project Management tools help projects run smoothly by cutting waste, solving problems, and keeping teams focused. Here are two of the most useful ones.
The Deming Cycle, also called Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA), was created by Dr. W. Edwards Deming in the 1950s. It’s a simple four-step method you can use again to make things better.
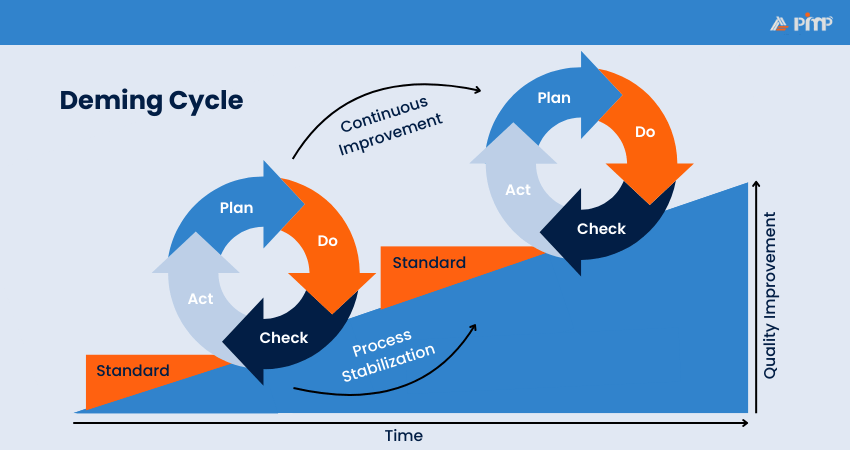
Here’s how it works:
1) Plan: Look at your work and find a problem that needs fixing
2) Do: Test a solution by trying it out on a small scale
3) Check: See if the solution worked or if changes are needed
4) Act: Put the improved solution into action for the whole team
It’s a cycle, which means once you finish, you can start again to keep improving. Many teams use PDCA because it’s easy to follow and works for almost any process.
Lean Six Sigma is another tool that mixes Lean’s focus on removing waste with Six Sigma’s focus on quality. One of its methods is called DMEDI, and it gives you five clear steps for managing projects.
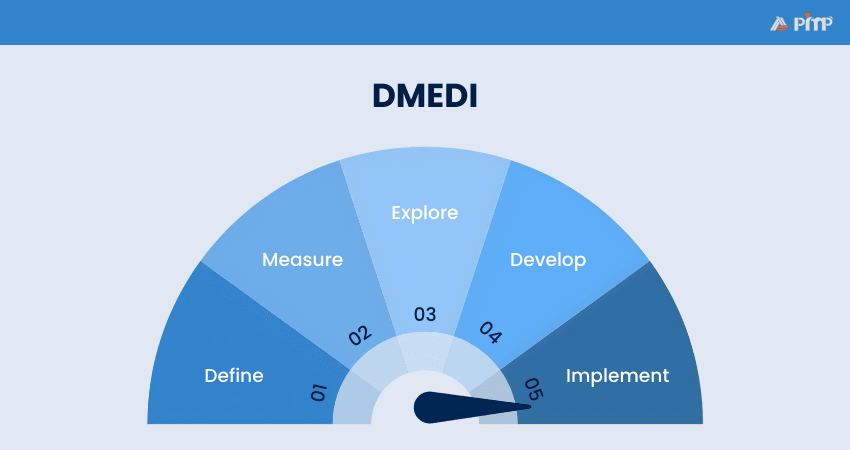
Here are the steps:
1) Define: Set your project goals
2) Measure: Decide how you’ll track success
3) Explore: Look for ways to improve your process
4) Develop: Build a detailed plan that works
5) Implement: Put your plan into action
Along with these steps, Lean Six Sigma uses extra tools like:
1) Value Stream Mapping (VSM): To see the full process and spot waste
2) Customer Feedback Surveys: To hear directly from users and improve value
3) Gantt Charts: To track project tasks and deadlines on a timeline
4) Root Cause Analysis (RCA): To dig into problems and find their real cause
5) Kanban Boards: To visualize tasks and make sure work flows smoothly
This mix of steps and tools helps teams reduce waste, make better plans, and deliver more value to customers.
Align your projects with strategy through expert training. Join our Portfolio Management Professional (PfMP)® Certification –Sign up now!
Lean Methodology makes projects easier and more successful by giving more value to customers while reducing waste and saving resources. Key advantages include:
Lean Project Management offers benefits that go beyond saving time and effort. It also improves how teams work and think. Here are its major benefits:
Lean encourages teams to stay open to change and look for better ways of working. Team members are free to share ideas, test improvements, and fix problems as they appear. Over time, this builds a habit of regular improvement of processes instead of following the outdated methods.
1) Encourages team members to suggest improvements
2) Supports flexibility in how work is done
3) Promotes learning from mistakes
4) Builds a mindset focused on continuous progress
Lean projects involve stakeholders and customers closely to make sure only useful work is done. Clear communication, shared planning, and regular feedback help everyone understand project progress. This visibility builds trust and ensures the final results match real customer needs.
1) Improves transparency in project activities
2) Keeps stakeholders informed and involved
3) Reduces misunderstandings and scope creep
4) Aligns deliverables with customer expectations
Lean reduces costs by avoiding unnecessary work and excess inventory. By producing only what is needed and when it is needed, teams prevent waste and rework. A strong focus on efficiency also helps organizations keep a close watch on spending.
1) Minimizes waste and rework
2) Reduces inventory and storage costs
3) Improves use of time and resources
4) Supports better cost control
Although Lean is effective, it also comes with some challenges. Here are the challenges that you need to consider:
Lean focuses on small improvements, which can sometimes make teams miss the overall project goals. Fixing one part of a process may create problems elsewhere if the wider impact is not considered. Regular reviews help keep improvements aligned with bigger objectives.
Lean avoids overproduction, which can make future demand harder to predict. When customer needs or market conditions change suddenly, teams may need to react quickly instead of planning ahead. Balancing flexibility with forward planning is important for long-term success.
Lean Project Management helps teams deliver real value while reducing waste and delays. By focusing on smooth workflows and continuous improvement, it ensures projects are efficient and effective. This approach empowers organizations to save time, cut costs, and achieve better results while keeping both customers and teams satisfied.
Becoming a Project Management professional with our Project Management Institute (PMI)® Certification – Join now!






© Copyright 2025. All rights reserved. Contact: PMP® TRAINING ACADEMY.


