







 10 Sep 2024
10 Sep 2024



There’s a universal truth in the world of Project Management: Uncertainty is the only certainty. While there's no one-size-fits-all solution to avoid uncertainties, Project Risk Management is the way to go. It's the art of anticipating challenges before they strike and turning potential threats into opportunities for more intelligent decisions.
From protecting budgets to building trust with stakeholders, mastering Risk Management can open doors to greater clarity and smarter solutions. This blog dives into the world of Project Risk Management, spotlighting its importance, challenges, tools, types and more. So read on and turn every risk into a stepping stone towards lasting success!
Table of Contents
1) What is Project Risk Management?
2) Why is Project Risk Management Important?
3) Types of Project Risks
4) Five Steps in the Project Risk Management Process
5) Benefits of Project Risk Management
6) Challenges in Project Risk Management
7) Tools and Software for Project Risk Management
8) Tips for Reducing and Managing Project Risks
9) Conclusion
Project Risk Management is a structured way of identifying, analyzing and addressing any potential events that could negatively affect a project’s objectives. This is a proactive approach that helps minimize threats while maximizing opportunities across the project lifecycle.
By anticipating possible challenges, managers can allocate the resources properly and make informed decisions to keep the projects on track. A strong Risk Management plan significantly reduces failures, cost overruns and schedule delays. When combined with the Six Sigma methodologies, it further boosts efficiency and enables teams to eliminate inefficiencies and lower overall project risks.
Risks can surface at any stage of a project’s lifecycle. Recognizing their types makes it easier to anticipate challenges early and implement strategies to minimize their impact. Here are some of the types:
External risks are driven by factors beyond organizational control. These might include:
1) Market fluctuations affecting project feasibility
2) Regulatory changes forcing adjustments
3) Severe weather disrupting schedules,
4) Supply chain interruptions delaying critical resources
Financial risks directly affect a project’s budget and resources. These may include:
1) Unexpected cost overruns
2) Sudden shifts in exchange rates for international projects
3) Vendor price hikes
4) Cash flow shortages that hinder progress
Technical risks arise when systems, tools, or expertise fall short. Examples include:
1) Software compatibility issues
2) Integration challenges between new and existing systems
3) Performance bottlenecks that delay outputs
4) Gaps in team skills that surface mid-project
Operational risks stem from daily project activities. Common issues include:
1) Staffing shortages when key members are unavailable
2) Inefficient processes slowing delivery
3) Communication breakdowns among stakeholders
4) Lapses in quality control without proper monitoring
Secure the spotlight of global recognition for your project leadership. Sign up for our Project Management Institute (PMI)® Certification now!
The Project Risk Management process involves identifying, evaluating, and addressing risks throughout the project lifecycle. This structured approach reduces the risks' impact on project objectives. Below are the five key steps to follow:
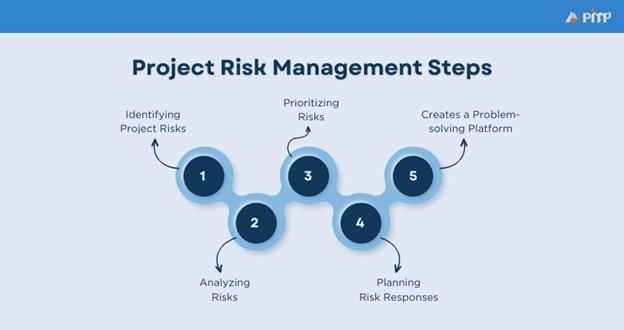
The first step is to identify potential risks that could affect the project. This requires a strong understanding of project objectives, timelines, and resources. Common techniques include:
1) Brainstorming: Engaging the team to generate a list of possible risks based on experience.
2) Checklists: Using lessons from past projects or industry standards to highlight recurring risks.
3) Expert Consultation: Seeking insights from subject matter experts with relevant experience.
4) SWOT Analysis: Evaluating strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to uncover potential risks.
After risks are identified, they must be analyzed to assess their likelihood and potential impact. This helps in prioritization and resource allocation. Two approaches are widely used:
1) Qualitative Analysis: Ranking risks as high, medium, or low based on probability and impact.
2) Quantitative Analysis: Using numerical techniques to measure probability and impact with greater precision.
Not all risks are equal; some require immediate action, while others can be monitored. Prioritization ensures attention is given to the most critical risks. Key factors include impact on project goals (timeline, cost, quality) and likelihood of occurrence. Methods include:
1) Risk Matrix: Mapping risks against likelihood and impact.
2) Risk Scoring: Assigning numerical values to calculate overall risk levels.
3) Pareto Analysis: Focusing on the few risks that cause most of the problems.
4) Decision Tree Analysis: Exploring different outcomes for complex projects.
5) Stakeholder Input: Considering perspectives from clients and team members for a holistic view.

Suitable response strategies are developed for each priority risk. These responses depend on the risk level, project goals and available resources. Strategies may involve:
1) Avoiding the risk
2) Mitigating its impact
3) Transferring responsibility
4) Accepting it with contingency measures
The final step is the ongoing monitoring of risks throughout the project. This includes:
1) Tracking known risks
2) Implementing response plans
3) Updating strategies as conditions change
4) Identifying new risks as they emerge
5) Continuous monitoring ensures the project remains resilient against evolving challenges.
Our Program Management Professional (PgMP)® Certification is your gateway to mastering enterprise-level transformation. Sign up now!
Some teams handle challenges smoothly while others struggle when they encounter issues. The difference often lies in effective Risk Management, which shapes how a team anticipates, prepares for and responds to uncertainty. Here are the key benefits:
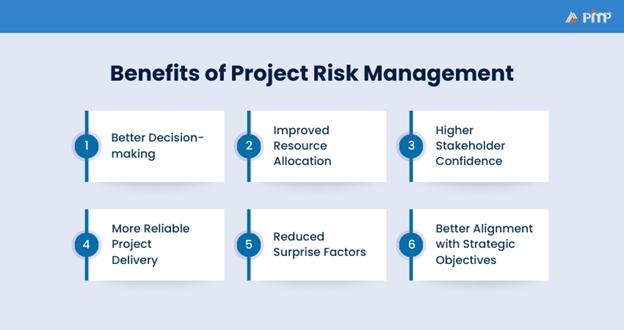
1) Better Decision-making: Awareness regarding potential risks leads to smarter strategies and a stronger ability to adapt as conditions change.
2) Improved Resource Allocation: With risks clearly prioritized, resources such as time, money, and skills can be directed where they matter most.
3) Higher Stakeholder Confidence: When stakeholders see that risks are being proactively managed, their trust and confidence in the team grow.
4) More Reliable Project Delivery: By controlling uncertainties, teams can deliver consistent outcomes and meet commitments as planned.
5) Reduced Surprise Factors: Teams are better prepared with contingency plans that enable them to respond swiftly and effectively to new challenges.
6) Better Alignment with Strategic Objectives: This alignment strengthens the value that projects deliver and supports broader business success.
Take control of project timelines with ease. Register for our PMI Scheduling Professional (PMI-SP)® Certification now!
Even with well-structured processes, Project Risk Management can face obstacles. Here are some common challenges to watch out for:
1) Hidden or Emerging Risks: Not all risks are visible at the start, and some appear unexpectedly as the project progresses. These can be difficult to predict and require constant vigilance.
2) Resource Constraints for Risk Management: Limited resources often mean prioritizing immediate tasks over long-term risk planning, which can leave gaps in protection.
3) Resistance to Change: Stakeholders or team members may resist adopting new processes. This reluctance can slow implementation, making it harder to adapt to risks in a timely way.
4) Overconfidence in Risk Assessments: Relying too heavily on initial assessments can create a false sense of security. This can lead to inadequate preparation for unexpected variables that may be overlooked.
5) Balancing Risk Management with Project Progress: Too much focus on Risk Management can delay some deliverables, while too little can leave a project vulnerable.

Here are some prominent tools for Project Risk Management that you can consider:
1) Microsoft Project: This is a widely used project planning and scheduling tool which has risk‐tracking. Besides helping managers plan tasks, resources and timelines, it allows recording and managing risks as part of the project plan. Its key Features include:
1) Risk register with the ability to record risks with fields like probability, impact, cost, trigger, mitigation & contingency plans.
2) Linking risks to specific tasks or activities, so you can see which tasks are exposed.
3) Views such as Gantt charts and critical path to help identify tasks with high potential risk in schedule.
4) Prioritization of risks via scoring (impact × probability), to focus effort where it matters most.
5) Tracking and reporting features to monitor the status of risks, track changes, assign owners etc.
2) Primavera Risk Analysis: This is a dedicated Risk Analysis tool created by Oracle focused especially on cost and schedule risks in large or complex projects and portfolios. It integrates with scheduling tools and helps in modelling uncertainty and forecasting risk through quantitative methods. Its key features include:
1) Monte Carlo simulation for schedule & cost risk assessment, to model uncertainty under various risk scenarios.
2) Schedule Check tool which validates schedule integrity and readiness for risk analysis by finding scheduling problems.
3) Quick Risk/Templated Quick Risk that allows applying standard uncertainty models to tasks without manually specifying detailed distributions for everything.
4) Risk Breakdown Structure (RBS) for organizing, categorizing and filtering risks.
5) Rich reporting through histogram/distribution graphs, tornado charts, scatter plots, and switching between cost and schedule views.
3) Wrike: Wrike is a more general Project Management platform with features that support Risk Management. It allows teams to incorporate risk‐related tracking and adjust as the project evolves. Its key features include:
1) Multiple views (Table, Kanban, Gantt) to visualize dependencies, delays and risk points.
2) Templates for Risks, Assumptions, Issues, Dependencies (RAID) logs to standardize and simplify risk tracking.
3) Dashboards & analytics to monitor potential risks, progress on mitigation plans and early warning signs.
4) Collaboration features so stakeholders can comment, share visibility into risks & action plans.
4) Monday.com: This is a flexible work and project collaboration platform. Its Work Management suite supports risk tracking, boards/templates, dashboards, risk registers etc. Its key features include:
1) Centralized risk register boards that capture risk details, assign owners, track status and update in real time.
2) Customizable boards and columns to fit your risk framework.
3) Dashboards and real‐time reporting for visualizing risk over multiple projects.
4) Templates like risk log, program risk register, RACI etc. to standardize workflows.
5) Automated insights that scan projects and highlight possible risks.
No matter how carefully you plan a project, unexpected challenges can still come up. The key is to stay proactive. Here are five essential tips to manage project risks:
1) Create a Strong Risk Management Plan: Clearly assign responsibilities, outline communication methods, and include strategies for continuous monitoring and control.
2) Keep the Risk Register Current: Maintain a detailed risk register that records all identified risks, their impact, and status. Regularly update it as circumstances change.
3) Understand Risk Events in Depth: Analyse each risk by exploring its causes, possible consequences, and likelihood of occurring.
4) Prioritize Proactive Action Over Reaction: By reducing reliance on reactive problem-solving, projects can minimize disruptions and maintain smoother progress.
5) Strengthen Project Management Expertise: Continually build your Project Management and risk handling skills through learning and professional development.
Project Risk Management is about steering projects with confidence, clarity and control despite uncertainties. By recognizing risks and embracing proactive strategies, your team can transform uncertainty into opportunity. Whether it’s protecting resources, satisfying stakeholders or achieving goals, effective Risk Management ensures that every project journey ends with success and lessons for the future.
Are you a beginner striving to become a confident Project Management professional? Sign up for our Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) ® Training now!






© Copyright 2025. All rights reserved. Contact: PMP® TRAINING ACADEMY.


