








Have you managed a project where deadlines were tight, goals kept shifting, and stakeholders demanded quick results? That’s where understanding What is Agile Project Management becomes essential. It grabs attention by addressing real challenges, sparks interest through adaptability, and builds desire for faster, value-driven results.
Agile empowers teams to work in short cycles, stay responsive, and deliver quality. With the right components and phases, you’ll soon see why Agile is transforming how modern projects succeed.
Table of Contents
1) What is Agile Project Management (APM)?
2) How does Agile Project Management Work?
3) Components of Agile Project Management
4) Phases of Agile Project Management
5) Key Principles of Agile Project Management
6) Agile Project Management Process
7) Benefits of Agile Project Management
8) Drawbacks of Agile Project Management
9) Comparing Agile Project Management and Waterfall Project Management
10) Conclusion
Agile Project Management (APM) is a structured yet flexible approach to managing projects emphasizing adaptability, collaboration, and customer value. It breaks down work into smaller, manageable iterations or sprints, allowing teams to deliver outcomes frequently and adopt results based on feedback. This continuous cycle of planning, execution, and evaluation promotes early delivery and ongoing improvement.
Unlike traditional Project Management, APM embraces change, even in later stages of a project, and encourages cross-functional teams to work collaboratively to meet evolving needs. By combining Agile Principles with control frameworks such as PRINCE2, Agile Project Management offers a balanced method for modern project environments.
Agile Project Management follows a structured yet flexible approach that enables teams to plan, execute, and deliver work in short, focused cycles. Here’s how each phase contributes to an efficient and adaptive workflow:
Agile Project Management begins with the Product Owner, who defines the overall vision and goals of the project. The Product Owner is responsible for identifying what needs to be built and translating that into a prioritised list of features, tasks, and requirements. This list is known as the Product Backlog, and it serves as the central source of work for the development team.
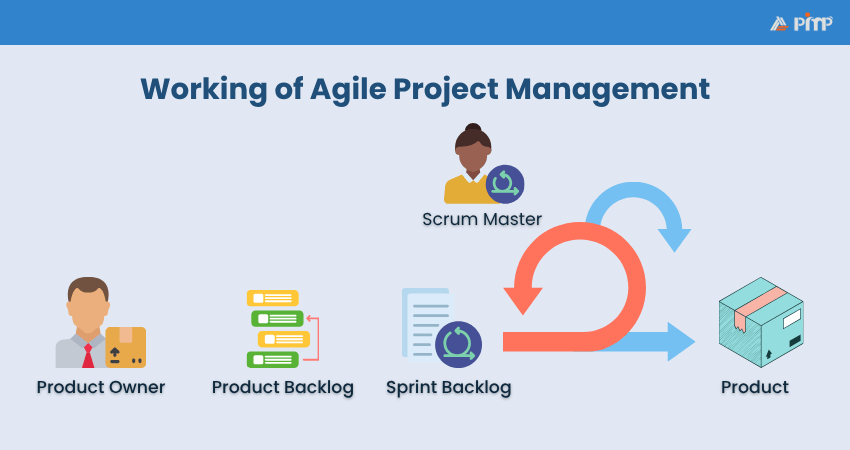
From the Product Backlog, a smaller selection of tasks is chosen for the next iteration, known as Sprint. These selected tasks form the Sprint Backlog. The team, with the help of the Scrum Master, plans how to complete these tasks within a set time frame, typically 1 to 4 weeks. The Scrum Master ensures that Agile principles are followed, supports the team by removing any blockers, and facilitates communication.
During the Sprint, the team works collaboratively, meeting daily for short stand-up meetings to track progress and address issues. At the end of the Sprint, a working product increment is delivered. This product is potentially shippable and adds value to the customer, even if it's just a small feature or improvement.
The cycle then repeats. Feedback from the stakeholders is reviewed, the Product Backlog is updated, and a new Sprint begins. This iterative process allows teams to adapt to change, deliver value early and often, and maintain close alignment with customer needs. Agile Project Management ensures continuous improvement, faster delivery, and better Risk Management.
Agile Project Management is built around several core components that enable flexibility, transparency, and rapid delivery. Below are the key elements that guide teams through effective agile execution.
User stories are short, user-focused descriptions of a feature or functionality. They help the team understand what the user needs, guide development priorities, and promote collaborative discussion around delivering valuable and usable outcomes.
Sprints are fixed, time-boxed iterations where Agile teams plan, develop, and deliver working features. Typically lasting 1 to 4 weeks, sprints allow for frequent feedback, adaptive planning, and continuous delivery of product increments.
Stand-up meetings are brief, daily check-ins where team members share progress, discuss obstacles, and coordinate tasks. These meetings encourage transparency, build accountability, and keep everyone aligned on sprint goals and daily priorities.
An Agile board visually represents task progress across stages such as To Do, In Progress, and Done. It enhances team visibility, helps track progress in real time, and ensures better workflow management and task clarity.
The backlog is a prioritised list of user stories, tasks, or features maintained by the Product Owner. It evolves continuously based on feedback, changing requirements, and business goals, ensuring the team focuses on the most valuable and relevant work.
Agile teams include a Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Developers. Each role supports the Agile process by managing requirements, facilitating progress, and delivering working software. Collaboration among these roles drives efficiency and project success.
Build real-world Agile capability through PMI-ACP® Certification – Explore Now!
Agile Project Management follows an adaptive and iterative process structured around key phases. Each phase supports continuous learning, delivery, and improvement throughout the project lifecycle:
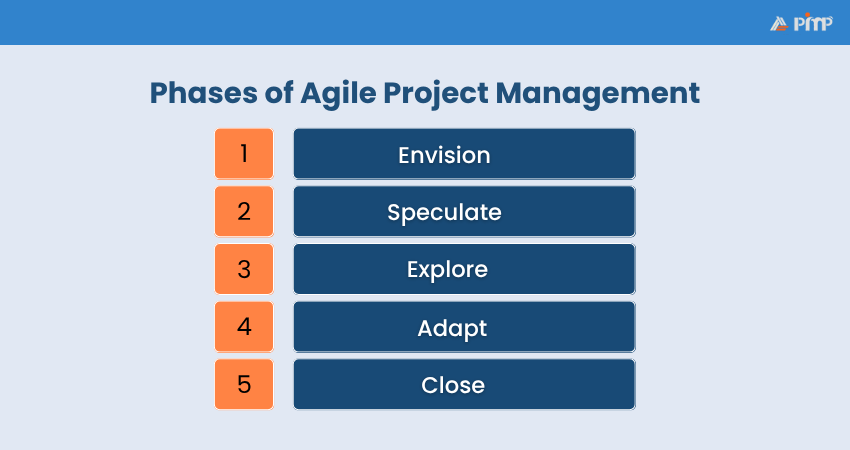
In this initial phase, the project vision, objectives, and high-level scope are defined. Stakeholders align on goals, key deliverables, timelines, and team roles to establish a shared understanding of success.
During the Speculate phase, the team develops a product roadmap, defines release plans, and prioritises the backlog. Risk assessment and rough estimates are made to plan early iterations and prepare for execution.
The Explore phase involves executing sprints or iterations to build and test working features. Teams collaborate closely, gather feedback, and refine the product continuously based on real user insights and changing needs.
In this phase, the team reviews sprint outcomes, stakeholder feedback, and performance metrics. Adjustments are made to the backlog, process, or priorities to ensure alignment with evolving business goals and user expectations.
The Close phase ensures all deliverables are completed and stakeholder requirements are met. Lessons learned are captured, team performance is reviewed, and the project is formally concluded with a final retrospective.
Agile Project Management is based on core principles that promote adaptability, collaboration, and value-driven delivery. These principles guide teams in executing projects effectively while responding quickly to change and customer feedback.
1) Agile ensures that all project activities are aligned with the organisation
2) Teams work on features that offer the highest value to stakeholders
3) Continuous stakeholder engagement helps maintain focus on customer needs
4) Business priorities are reassessed frequently to stay relevant
5) Every decision is aimed at maximising return on investment
1) Agile promotes early and frequent delivery of working product increments
2) Short development cycles help teams release features quickly
3) Regular releases allow stakeholders to see progress and provide input
4) Timely delivery reduces the risk of project delays
5) Early feedback helps identify and correct issues sooner
1) Agile encourages close collaboration among cross-functional team members
2) Teams share ownership of outcomes and work collectively toward goals
3) Stakeholders are involved throughout the project to maintain alignment
4) Continuous interaction builds trust and enhances problem-solving
5) A collaborative environment leads to better quality and faster decisions
1) Agile delivers work in small, manageable chunks that add up over time
2) Each increment is usable and contributes to the final product
3) Features are tested and reviewed after every iteration
4) This approach reduces complexity and makes progress visible
5) It ensures frequent delivery of customer-ready solutions
1) Agile projects move forward through repeated cycles of planning and delivery
2) Each iteration builds on the last, refining features and processes
3) Teams adapt based on feedback from previous cycles
4) Continuous improvement is embedded into each phase of work
5) Iterative progress supports flexibility and learning
1) Agile relies on transparent and frequent communication among all participants
2) Daily stand-up meetings help teams stay aligned and informed
3) Visual tools like task boards make work visible to everyone
4) Regular updates prevent misunderstandings and confusion
5) Clear communication builds trust and improves coordination
1) Agile maintains discipline through defined roles and responsibilities
2) Time-boxed sprints provide structure and focus to the work
3) Teams track progress using measurable metrics and reviews
4) A prioritised backlog ensures that work stays on track
5) Control is maintained without sacrificing flexibility and innovation
Explore Project Management basics and earn industry recognition with PMI Project Management Ready® Certification - Register now!
The Agile Project Management process is divided into key stages, starting from planning and continuing through execution and reflection. Each step plays a vital role in ensuring adaptability and consistent value delivery.

Project planning in Agile involves defining the high-level goals, scope, stakeholders, and success criteria. Unlike traditional planning, Agile planning is lightweight and flexible, focusing on creating a shared vision and setting priorities without locking in rigid timelines.
The project begins with high-level planning. The team and stakeholders define the goal: build a secure, user-friendly mobile banking app. Key features like login, balance view, fund transfers, and bill payments are identified. The scope is intentionally broad to allow flexibility as development progresses.
The product roadmap outlines the long-term vision and strategic direction of the product. It helps prioritize key features and milestones over time, ensuring alignment between business goals and development activities, while remaining flexible to accommodate evolving needs.
The Product Owner creates a roadmap outlining when major features will be developed. For example, Phase 1 will include user login and balance viewing, Phase 2 will add fund transfers, and Phase 3 will introduce bill payments. This helps align the team with business priorities and user needs.
Release planning defines how and when increments of the product will be delivered. It involves selecting features from the product backlog, estimating delivery timelines, and setting expectations with stakeholders. The goal is to deliver usable value in each release.
In the release planning stage, the team decides to release the app in three main increments. The first release will provide basic login and account balance features. This staged release strategy allows the team to gather feedback early and refine upcoming features accordingly.
Sprint planning occurs at the start of each iteration. The team selects items from the backlog to work on during the sprint and defines the sprint goal. Tasks are broken down, responsibilities are assigned, and a clear plan is set for execution.
For the first sprint, the team selects user stories related to secure login and viewing account balances. Tasks such as UI design, API integration, and security checks are broken down. The team defines the sprint goal: deliver a working login screen with real-time balance display.
Daily stand-ups are short team meetings held every day during the sprint. Each team member shares what they worked on, what they plan to do next, and any obstacles. These meetings improve communication and keep the team aligned and focused.
Each day, the team holds a stand-up meeting. One developer reports completing the login UI and plans to start integrating encryption. Another mentions a blocker with API response delays. The Scrum Master takes note of the issue and works to resolve it so the sprint stays on track.
At the end of each sprint, a Sprint Review is held to showcase completed work to stakeholders and gather feedback. This is followed by a Retrospective, where the team reflects on what went well, what didn’t, and how to improve in the next sprint.
At the end of the sprint, the team demonstrates the login and balance features to stakeholders in the Sprint Review. Stakeholders suggest adding biometric login in a future sprint. In the Retrospective, the team discusses what went well and decides to improve sprint planning by refining task estimates next time.
Agile Project Management offers several key advantages that contribute to project success. Below are the top benefits that make Agile a preferred approach for modern, fast-paced project environments.
a) Faster Value Delivery: Agile allows teams to release usable product features early, helping businesses gain quicker returns and user feedback.
b) Greater Flexibility and Adaptability: Teams can easily adjust to changing requirements, priorities, or customer needs throughout the project lifecycle.
c) Improved Stakeholder Satisfaction: Frequent updates, demos, and reviews keep stakeholders engaged and ensure their expectations are met.
d) Enhanced Team Collaboration: Agile promotes open communication, shared responsibility, and strong coordination within cross-functional teams.
e) Higher Product Quality: Continuous testing and regular feedback help detect issues early, resulting in more reliable and refined
Despite its strengths, Agile Project Management may not be ideal for every project or team. Below are the top challenges often associated with Agile:
a) Challenging Scope Management: The flexibility of Agile can lead to frequent requirement changes, making it difficult to maintain clear scope, timelines, and budgets.
b) High Team Involvement Required: Agile demands continuous collaboration, which can be challenging for teams with limited time, availability, or communication experience.
c) Limited Project Documentation: The focus on working solutions over documentation can result in insufficient records for future reference or team transitions.
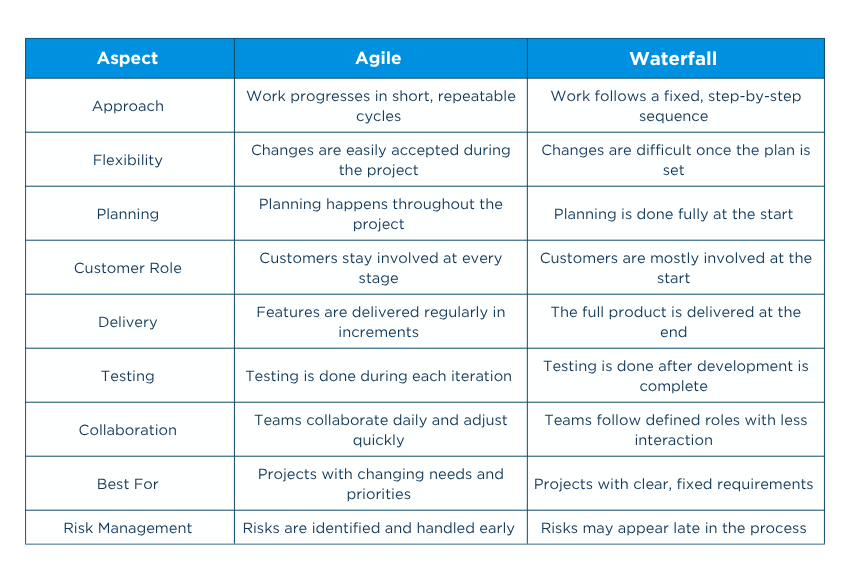
The table below outlines the key differences between Agile and Waterfall Project Management across various aspects to help you understand which approach suits your project best:
Agile Project Management empowers teams to seize opportunities through rapid delivery, adapt to shifting needs, achieve customer satisfaction with continuous feedback, and refine processes for lasting success. It is a flexible, iterative approach that emphasizes collaboration, customer involvement, and the ability to respond quickly. This method drives consistent value, helping organizations thrive in dynamic conditions and deliver quality outcomes aligned with project goals.
Build future-proof project skills, start your journey with Project Management Institute (PMI)® Certification – Join today!






© Copyright 2025. All rights reserved. Contact: PMP® TRAINING ACADEMY.


