







 10 Sep 2024
10 Sep 2024



The Project Management Triangle is like the balancing act every Project Manager must master. It's got three sides that streamlines one mission. Time, cost and scope form this non-negotiable trio, each tugging at the others as teams race toward successful delivery. Change one, and the entire structure shifts.
But rather than a constraint, the Project Management Triangle becomes a beacon, helping leaders make smart trade‑offs and realistic decisions. In this blog, we’ll unpack its purpose and explore real‑world examples that bring this framework to life. So read on!
The Project Management Triangle represents three key factors that influence project quality: scope, cost, and time. These elements are closely connected, meaning a change to one will impact the others. The triangle shows that if one factor shifts without adjusting the remaining two, balance is lost and project quality can decline.
Maintaining this balance is essential to keep the project on track. Often called the iron triangle, it highlights a Project Manager’s responsibility to manage scope, budget and schedule carefully to deliver quality outcomes while meeting deadlines and cost limits.
The Project Management Triangle is more than a concept; it is a practical framework that helps Project Managers balance priorities and make informed trade-offs. It supports decision-making when challenges arise and ensures that expectations and outcomes remain aligned. Specifically, it helps ensure that:
a) Expectations remain realistic based on time, cost and scope limitations.
b) Stakeholders understand how changes affect overall project success.
c) Resources and workflows are managed efficiently without compromising objectives.
d) Risks are identified early and managed through informed adjustments to project Constraints.
e) Project quality is maintained by balancing delivery speed, budget control, and defined requirements.
Manage portfolios and maximize value with our like a pro with our Portfolio Management Professional (PfMP)® Certification - Sign up now!
To manage all three sides of the Project Management Triangle effectively, a Project Manager must clearly understand each constraint and know where flexibility is possible.
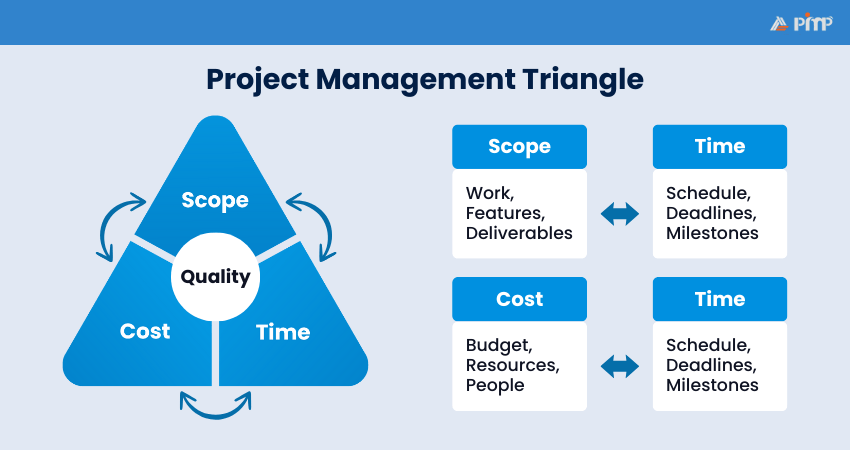
In the Project Management Triangle, cost refers to more than just money. It includes all resources needed to deliver the project, such as people, tools, equipment and facilities. While not all costs are direct expenses, most can be linked back to financial impact.
Elements of cost may include:
a) Financial budget
b) Team size
c) Tools, equipment, and workspace
d) Operational opportunities and support needs
Time covers both the total duration of the project and how working time is structured. Managing time effectively may involve adjusting deadlines, reallocating effort, or revising planning phases. If the scope increases or the budget is reduced, the project timeline often needs to be adjusted. Elements of time include:
a) Overall project duration
b) Hours allocated to tasks
c) Team schedules and calendars
d) Time for planning and decision-making
e) Number of project stages or phases
Scope defines the size and depth of a project, including what will be delivered and the level of quality expected of it. As the scope expands, more time and resources are usually required to complete the work. To avoid scope creep, it is essential to finalise requirements early and gain stakeholder approval before work begins.
Key elements of scope include:
a) Quantity of deliverables
b) Quality standards
c) Project complexity
d) System capacity or performance strength
e) Level of detail
f) Number and complexity of features
Managing the Project Management Triangle requires careful planning and constant balancing of scope, time and cost. Here are the main factors that help Project Managers deliver successful outcomes:
Open and transparent communication with stakeholders is essential. Clearly explaining limitations, priorities, and trade-offs helps set realistic expectations from the outset. When stakeholders understand how changes may affect quality, timelines, or budgets, trust is strengthened and misunderstandings are minimised.
Every project carries risks such as budget pressure, delays, changing requirements, etc. Identifying these risks early on and preparing response plans helps prevent disruptions and keeps the project moving smoothly.
Change is unavoidable in most projects. A structured process for reviewing and approving changes ensures that the adjustments are controlled and do not destabilise the project. This approach protects objectives and prevents unnecessary rework.
Project Managers often use flexible frameworks such as Agile or Lean to respond to shifting constraints. By breaking work into smaller phases or iterations, teams can adapt scope while still maintaining control over time and cost. This approach supports responsiveness without sacrificing delivery discipline.
Digital tools help track progress across scope, cost, and time. They provide visibility, support better planning, and offer insights that help Project Managers address issues early, before they affect delivery.
Embrace PgMP® and orchestrate multiple projects with confidence. Sign up for our Program Management Professional (PgMP)® Certification now!
Different Project Management approaches emphasise different elements of the Project Management Triangle. Because of this, each method balances time, cost and scope in its own way. Here are some commonly used Project Management methods to adapt the triangle to your management style:
These methods suit projects with tighter budgets and more flexibility around timelines. The focus is on efficient use of resources and cost control.
a) Waterfall: Project phases are completed sequentially. Delays in one phase affect all following stages, making this method suitable where timelines can be adjusted.
b) Lean: Lean aims to minimise waste and reduce unnecessary resource usage. Scope or timelines may be adjusted to ensure the project stays within budget.
c) PRINCE2: PRINCE2 uses a structured, stage-based approach with strong governance and control. It focuses on clear roles, defined stages and business justification. This helps manage costs while allowing flexibility in scheduling.
When speed and responsiveness are priorities, these methods help reduce delays and keep work progressing efficiently.
a) Agile: Agile supports rapid adaptation via short work cycles. Teams can respond to changes quickly with minimal impact on cost or timelines, often by using dedicated agile tools.
b) Scrum: Scrum is a framework within Agile that relies on short sprints and regular team check-ins to reduce delays and maintain steady progress. This is particularly useful in Software Development.
c) Kanban: Kanban uses visual workflows and continuous delivery to limit the work in progress and reduce bottlenecks. This helps the team complete tasks faster.
d) Scrumban: Scrumban combines Scrum’s regular reviews with Kanban’s continuous flow. It allows teams to stay flexible while minimising delays and work-in-progress time.
The Project Management Triangle offers a practical framework for balancing scope, time and cost. Here are the major benefits of applying it in project delivery.

Understanding how changes affect each constraint helps identify risks early. With regular monitoring, potential issues can be addressed before they grow into major problems, allowing timely corrections and smoother delivery.
Setting realistic boundaries helps align teams as well as the stakeholders. Clear agreement on deliverables, constraints and trade-offs reduces confusion and minimises conflicts throughout the project lifecycle.
Time, budget and people can be managed more efficiently. When resources are allocated wisely, waste is reduced, productivity improves, and projects run more smoothly.
A structured framework makes it easier to track progress and identify issues early. Project Managers can monitor performance, address bottlenecks, and make necessary adjustments to keep the project on track.
The triangle helps teams stay focused on what matters most. By clearly defining priorities, project goals are structured more effectively, thus ensuring that critical tasks receive the attention and resources they need.
The Project Management Triangle reminds us that every decision shapes a project’s outcome. When time, cost and the scope pull in different directions, a thoughtful balance becomes the key to success. Understanding this framework empowers teams to adapt with confidence. As you navigate your next project, let the triangle guide smarter choices and smoother execution.
Stand out in a world of Project Managers with our range of Project Management Institute (PMI)® Certification - Sign up now!






© Copyright 2025. All rights reserved. Contact: PMP® TRAINING ACADEMY.


