







 10 Sep 2024
10 Sep 2024



Projects rarely go exactly as planned. One moment, work is on track, and the next, new requests, shifting priorities, and unexpected challenges arise. As these changes add pressure and uncertainty, understanding What is Agile Methodology becomes essential. Agile helps teams remain flexible, adapt quickly and continue delivering value even as project needs evolve.
In this blog, you will explore What is Agile Methodology, how it works, the principles behind it, and when it should be used. Read on to learn more!
Agile Methodology is a flexible Project Management approach that emphasizes adaptability, collaboration, and continuous improvement. It divides projects into smaller, manageable phases called iterations or sprints, enabling teams to respond quickly to changing requirements and customer feedback.
Unlike traditional methods, Agile encourages continuous testing and development throughout the project lifecycle, resulting in higher-quality outcomes. While it is widely used in software development, Agile also benefits other industries that require dynamic solutions by promoting teamwork, transparency, and faster value delivery.
After understanding what is Agile methodology, the following principles explain how Agile is applied in real-world projects. Below are the core principles that define Agile practices:
1) Deliver Value Early and Often: Teams aim to satisfy the customer by providing useful outputs regularly so they can see progress and give timely feedback.
2) Accept and Adapt to Changing Requirements: Agile welcomes changes at any stage of the project, allowing the final product to meet real customer needs.
3) Release Working Software Frequently: Small, functional pieces of the product are delivered in short cycles instead of waiting until the end.
4) Encourage Daily Collaboration Between Business and Developers: Regular communication helps teams stay aligned with goals and solve issues quickly.
5) Build Projects Around Motivated People: Support teams with the resources they need and trust them to deliver quality results.
6) Use Direct Conversation as the Best Form of Communication: Communicating in person or through live discussions leads to faster and clearer understanding.
7) Measure Progress Through Working Software: Real, usable output is the true sign of project success rather than documents or reports.
8) Promote a Steady and Sustainable Pace: Teams should work at a consistent speed that avoids burnout and maintains quality.
9) Prioritize Technical Excellence and Good Design: Strong engineering practices and thoughtful design improve flexibility and maintainability.
10) Keep the Work Simple: Focus on maximising value by eliminating unnecessary tasks and effort.
11) Encourage Self-organizing Teams: Teams decide how to manage their work, leading to better solutions and stronger ownership.
12) Reflect Often and Improve Continuously: Teams regularly review their process and make adjustments to work more effectively.
Several frameworks exist within the Agile Methodology, each tailored to specific project needs. The following are the most commonly used Agile methodologies:
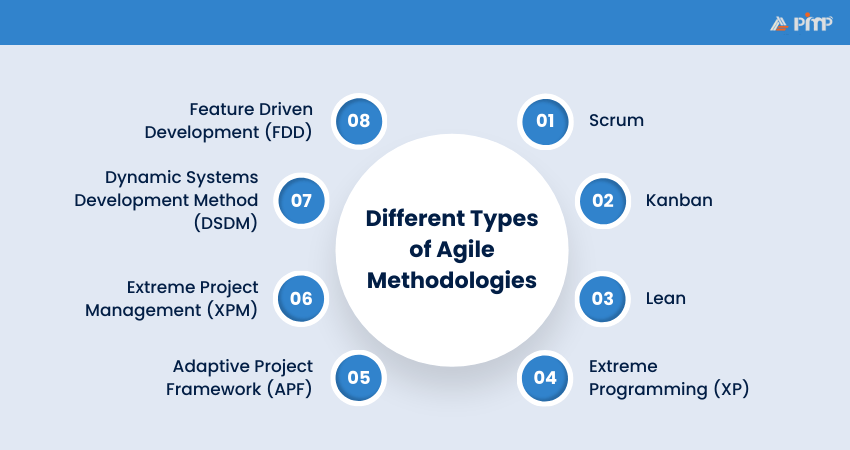
Scrum is one of the most accepted Agile frameworks, structured around short, time-boxed cycles called sprints. Each sprint takes a few weeks, during which specific tasks are completed, and at the end of each cycle, a review takes place to assess progress. Scrum emphasizes job roles such as the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team and relies heavily on daily stand-up meetings to ensure alignment.
Kanban focuses on visualizing the flow of tasks through a project. The primary tool used is a Kanban board, which divides tasks into columns representing different stages of completion. It emphasizes continuous delivery and encourages limiting work in progress to improve efficiency. Kanban is highly flexible and can be implemented in various project types, not just Software Development.
Lean methodology eliminates waste, streamlines processes, and enhances value creation. Originating from manufacturing, it is focused on reducing unnecessary steps in the workflow, maximizing efficiency, and focusing on value-added activities. The principles of Lean can be applied to Product Development and service-oriented projects.
Extreme Programming (XP) is an Agile framework that heavily emphasizes technical excellence, continuous feedback, and frequent software releases. XP encourages close association between developers and customers, with practices like pair programming, Test-driven Development (TDD), and refactoring at the core of its methodology. It aims to produce high-quality, scalable software quickly.
Adaptive Project Framework (APF) is an Agile approach for projects with high uncertainty or complex requirements. It is highly flexible, with continuous adaptation to changes in the project environment. APF encourages incremental progress and ongoing stakeholder collaboration to adapt to evolving project needs.
Extreme Project Management (XPM) suits complex, uncertain projects where constant change makes fixed plans unworkable. Teams adapt continuously, using trial-and-error and short, iterative sprints to test ideas, revisit decisions, learn quickly, and adjust direction as the project evolves.
The Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM) is a structured Agile approach covering the full project lifecycle. Its four phases include assessing feasibility, creating functional prototypes, designing and building the solution in iterative cycles, and finally implementing the product. This framework keeps projects flexible while ensuring alignment with business goals.
Feature Driven Development (FDD) is an Agile method focused on building clearly defined software features in short, iterative cycles. Customer feedback guides which features are prioritized, keeping development aligned with real needs. Frequent updates help teams spot issues early and fix them quickly, maintaining steady project progress.
Implementing Agile Methodology requires thoughtful consideration and strategic planning. The following steps outline how Agile Methodology can be effectively integrated into projects:
Selecting the right Agile framework is crucial to the success of a project. Project size, complexity, and team structure should be considered when choosing between Scrum, Kanban, Lean, or other Agile approaches.
An effective Agile team consists of individuals with complementary skills and a shared commitment to collaboration. Team members should be empowered to make decisions, and close collaboration should be maintained throughout the project lifecycle.
Although Agile is iterative, defining clear milestones and objectives is important. This helps the team keep focused and ensures the project progresses in the right direction.
Engaging stakeholders throughout the project is essential for ensuring that it meets their needs. Regular communication and feedback loops are crucial for managing expectations and making necessary adjustments.
In Agile projects, success is measured by the value delivered to customers. Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), user satisfaction, and the effectiveness of each iteration helps determine the project’s overall success.
Build strong project skills and boost your career with PMI Project Management Ready® Certification – Join now!
Agile Methodology is ideal for projects that demand flexibility, rapid iteration, and continuous feedback. It thrives in environments where requirements are unclear or frequently changing. Consider Agile when innovation, fast development or constant stakeholder involvement is crucial throughout the project lifecycle. Below are a few parameters to consider:
1) Suitable for projects with evolving or unclear requirements
2) Best for fast-paced, high-innovation environments
3) Effective when continuous feedback from stakeholders is necessary
4) Ideal for projects where rapid iteration is critical to success
5) Works well when flexibility is needed to adapt to changes
6) Beneficial for projects that require frequent testing and refinement
The Agile Methodology follows a cycle that ensures iterative and incremental progress. The following phases are typically observed in Agile projects:
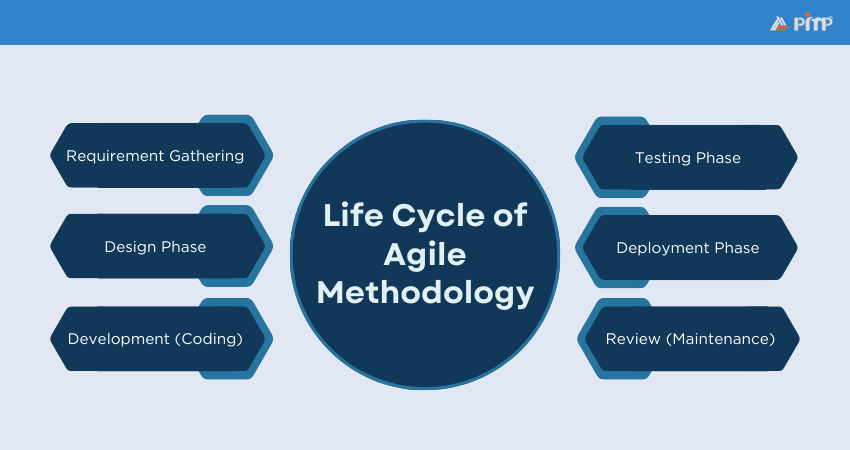
a) Focuses on high-level requirements instead of an exhaustive list
b) Identifies critical features that add value to the product
c) Requirements are refined and adjusted throughout the project
d) Prioritizes features that align with user needs and goals
e) Gathers stakeholder input early for clearer project direction
f) Establishes the foundation for project scope and functionality
a) Design evolves iteratively, adapting as the project progresses
b) Feedback from stakeholders influences design changes
c) Agile design focuses on flexibility, unlike traditional methods
d) Regular updates ensure the design aligns with user expectations
e) Team collaboration enhances design refinement throughout the process
f) The design phase continues alongside development
a) Coding occurs in short, manageable cycles, focusing on specific features
b) Each cycle prioritizes building features that meet the requirements
c) Teams collaborate to ensure alignment with gathered requirements
d) The development process is flexible, responding to feedback quickly
e) Code is tested frequently to ensure functionality and quality
f) Short cycles help maintain focus and momentum in development
a) Testing occurs continuously alongside development
b) Each iteration undergoes testing to meet quality and requirement standards
c) Continuous testing ensures the timely identification of issues
d) Early feedback from testing helps improve software features
e) Agile testing focuses on validating functionality incrementally
f) Testing involves all team members for comprehensive quality checks
a) Deployment happens incrementally, delivering software faster
b) Features are rolled out as they are developed and tested
c) Agile deployment allows users to access software quickly
d) Updates and improvements are delivered in smaller, frequent releases
e) Incremental deployment helps gather early user feedback
f) Continuous delivery ensures quicker adaptation to user needs
a) Maintenance is a continuous process rather than a separate phase
b) User feedback is gathered post-deployment for ongoing improvements
c) Regular reviews ensure the software evolves with user needs
d) Agile maintenance includes frequent updates and feature refinements
e) The team adjusts the product based on real-time user feedback
f) Ongoing collaboration ensures the software remains relevant and effective
Take the next step in your career with PMP Certification – Join now!
Here are the four key pillars of Agile Methodology:
Agile Methodology places strong emphasiz on the people doing the work. It values collaboration, communication, and adaptability over strict processes or specific tools. When individuals are empowered to make decisions and work closely together, the team becomes more resilient to challenges and change, resulting in better project outcomes.
Instead of being confined by predefined tools or procedures, Agile encourages flexibility and problem-solving by the team. The focus on individuals fosters a culture of trust and creativity, allowing the team to respond to new information quickly and efficiently, ensuring that the project remains on course despite evolving demands.
In Agile, the priority is to deliver working software rather than produce large amounts of documentation. Documentation is still used, but it supports the work rather than slowing it down. The focus remains on creating functional, user-ready features that show real progress, allowing the team to move forward quickly instead of getting stuck in lengthy paperwork.
This approach encourages iterative development, with the team continuously delivering usable features and refining the product. By prioritizing software functionality, Agile ensures that each increment adds value, meets customer expectations, and aligns with project goals, ultimately improving the product's quality and relevance.
Agile Methodology encourages continuous collaboration with customers, recognizing that their needs change over time. Instead of following rigid contract terms, Agile supports a partnership where customers stay involved and help shape the product as it evolves, ensuring it meets their expectations more effectively.
By engaging customers regularly, Agile ensures that the product continuously reflects their input, addressing any emerging concerns or new requirements. This collaboration strengthens customer relationships, improves product quality, and ensures the final deliverable meets user needs and expectations.
Agile values adaptability and flexibility instead of rigidly following predefined plans. While traditional methods rely on fixed approaches, Agile accepts that change is natural and should be embraced. The focus is on delivering value efficiently and adjusting the process as the project evolves.
This pillar ensures the project can evolve in response to new insights, customer feedback, or market shifts. By adapting to change, Agile teams can pivot, refine the product, and continuously improve their approach, ensuring that the final result remains relevant, functional, and aligned with the client’s goals.
Master Agile Project Management with PMI-ACP Certification – Start today!
Agile offers several advantages over traditional Project Management methods:
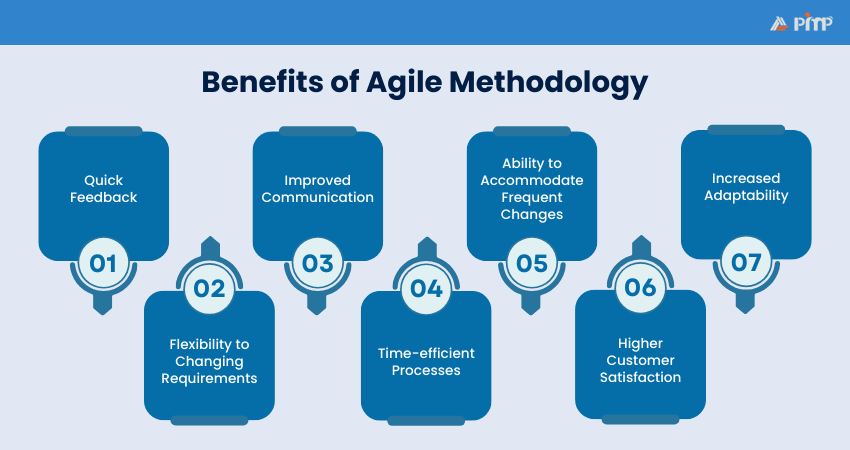
a) Regular feedback loops help identify issues early in the project
b) Stakeholders are engaged throughout, ensuring their concerns are addressed promptly
c) Enables timely adjustments to improve the final product
d) Short feedback cycles lead to better alignment with user needs
e) Iterative testing provides immediate insights into the product’s functionality
f) Frequent reviews allow for a responsive and Agile Development process
a) Agile allows for easy adaptation to shifting project requirements
b) Teams can adjust priorities based on evolving stakeholder needs
c) Flexibility ensures the project remains aligned with business goals
d) Changes can be incorporated without disrupting the entire workflow
e) Agile teams are equipped to handle both minor and major adjustments
f) Revisions are made with minimal delay, keeping the project on track
a) Daily stand-up meetings encourage ongoing team collaboration
b) Clear communication channels ensure transparency between all team members
c) Regular interaction with stakeholders leads to a better understanding of requirements
d) Open feedback loops foster a culture of trust and clarity
e) Collaborative tools improve information sharing and decision-making
f) Agile practices ensure all team members are aligned and informed
a) Agile focuses on delivering small, valuable increments of work
b) Prioritization ensures that the most important tasks are tackled first
c) Short sprints enable quicker delivery and faster time-to-market
d) Continuous testing and improvement enhance overall efficiency
e) Iterative work processes reduce waste and maximize productivity
f) Time is optimized by focusing on essential features and user needs
a) Agile is built to embrace change, allowing for quick adaptation to new needs
b) New requirements or changes can be easily incorporated into the project
c) Agile teams focus on delivering value regardless of shifting priorities
d) Adaptability ensures the product evolves with market or user demands
e) Frequent changes are managed through flexible planning and sprint adjustments
f) Changes do not disrupt the overall project flow or timeline
a) Agile delivers incremental value, ensuring early and continuous benefits to customers
b) Regular involvement of customers allows them to influence Product Development
c) Timely updates and frequent releases keep customers engaged and informed
d) Agile practices focus on meeting customer expectations and improving user experience
e) Regular feedback allows teams to fine-tune the product to customer preferences
f) Delivering high-quality, relevant features boosts overall satisfaction
a) Agile teams can quickly pivot based on Project Developments or market changes
b) The methodology encourages a growth mindset, where adaptability is key
c) Teams are more prepared to face unforeseen challenges and opportunities
d) Flexibility ensures projects can respond to both internal and external shifts
e) Agile’s iterative nature makes incorporating lessons learned along the way easier
f) Increased adaptability helps organizations stay competitive and responsive to change
Enhance your Business Analysis skills with PMI-PBA Certification – Register now!
While Agile offers several benefits, it is not without its challenges.
a) Lack of Clear Project Scope: Early stages of Agile projects may lack detailed scope, making planning challenging.
b) Requires Highly Skilled Team Members: Agile success depends on team expertise and the ability to work collaboratively.
c) Potential for Scope Creep: The iterative approach can lead to scope expansion as requirements evolve continuously.
d) Resource Intensity: Frequent revisions and updates demand substantial time and resources from the team.
Agile Methodology continues to shape how modern teams adapt, collaborate, and deliver value quickly. By understanding What is Agile Methodology, you can adopt a flexible way of working that supports constant improvement. As projects become more dynamic, Agile remains a powerful approach for achieving clarity, speed, and meaningful results.
Advance your Project Management career with CAPM Certification Training – Join today!






© Copyright 2025. All rights reserved. Contact: PMP® TRAINING ACADEMY.


