









Projects rarely fail overnight. They unravel through overlooked risks, unresolved issues and hidden dependencies. RAID in Project Management brings clarity to it all by turning such uncertainty into visible, manageable insights. It provides a structured lens to capture what could go wrong, what is being assumed, what is already happening, and what relies on something else.
In this blog, we will explore what RAID in Project Management means and how to perform it effectively for stronger planning, control and decision-making outcomes. So read on, master the art of project resilience and make sure project risks don't sneak up on you like uninvited guests!
RAID in Project Management is a simple framework used to track and manage four critical areas of a project: Risks, Assumptions, Issues, and Dependencies. It is commonly recorded in a RAID log, which acts as a central document for identifying problems, monitoring active challenges, documenting uncertainties, and understanding task relationships.
By maintaining a RAID log, Project Managers gain visibility into what might go wrong (risks), what is being assumed (assumptions), what is already happening (issues), and what tasks rely on others (dependencies). This helps teams stay organized, make informed decisions, and address problems before they impact project delivery.
The RAID framework is built around four key elements: Risks, Assumptions, Issues, and Dependencies. Each element plays a specific role in helping project teams understand and manage challenges throughout the project lifecycle. Here we explore each element in detail:
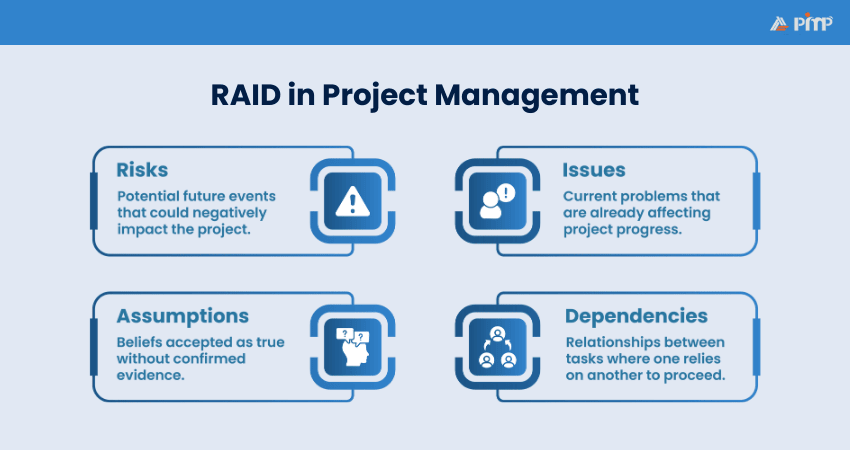
1) A risk is an uncertain event or condition that can impact the project objectives if it occurs.
2) Proper Risk Management focuses on identifying, analyzing and prioritizing potential risks.
3) Common project risks include budget overruns, scope creep and resource shortages.
4) Risks are evaluated based on their likelihood and potential impact on project goals.
5) Techniques such as risk matrices, Expected Monetary Value (EMV) analysis and decision trees help prioritize the risks that require immediate attention.
1) Assumptions refer to beliefs accepted as true without any confirmed evidence at the time of decision-making.
2) They support project planning and guide decisions while highlighting the areas of uncertainty.
3) Common assumptions relate to resource availability, stakeholder commitment and market stability.
4) Assumptions should be clearly documented to maintain transparency.
5) Regular review and validation ensure assumptions remain accurate as the project progresses.
1) Issues are problems that have already occurred and are impacting project performance.
2) Early identification and categorization of issues help minimize disruption and delays.
3) Issues can be identified through team meetings, progress reports and stakeholder feedback.
4) A structured resolution approach includes clear ownership assignment and root cause analysis.
5) Developing action plans and documenting resolutions supports timely control and future improvement.
1) Dependencies define the relationships where one project task depends on another.
2) Good Dependency Management supports accurate scheduling and smooth execution.
3) Common types include mandatory, discretionary and external dependencies.
4) Mapping task relationships helps identify sequencing requirements.
5) The right Project Management tools and clear stakeholder communication reduce delays and misalignment.
RAID Analysis enables early identification and evaluation of potential project risks. This reduces the chances of cost overruns, schedule delays and quality shortfalls. It prompts Project Managers to examine and validate assumptions regularly. This reduces the risk of decisions being driven by inaccurate or outdated information.
Additionally, RAID Analysis helps clarify dependencies, ensuring correct task sequencing and optimal resource allocation, which improves execution flow. And it provides a clear structure for discussing risks, assumptions, issues and dependencies with teams and stakeholders.
See the big picture, shape the future of your business. Become a portfolio visionary with our Portfolio Management Professional (PfMP)® Certification - Sign up now!
RAID Analysis follows a structured approach to identifying and managing Risks, Assumptions, Issues, and Dependencies within a project. Here's how you can perform the ideal RAID Analysis:
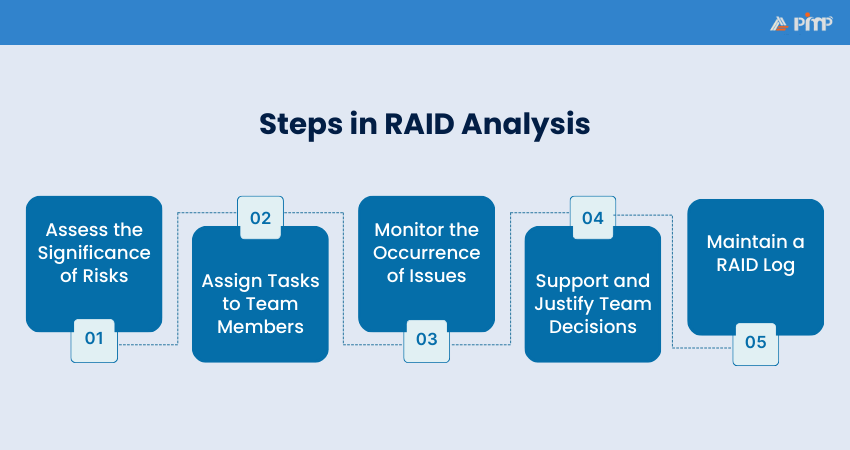
Not every risk affects a project in the same way. Some have little impact, while others can seriously disrupt your progress. Start by assessing the likelihood of each risk and its potential impact on project goals. Focus first on risks that are both high impact and high probability, as these need immediate attention.
After identifying the risks, assumptions, issues and dependencies, assign clear responsibilities to your team members. Match the tasks to individual skills and experience and clearly explain what each person is responsible for. Clear delegation helps ensure every RAID element is actively managed.
Problems can arise at any stage of a project, so issues must be tracked closely. Review their status regularly, note any changes and follow progress until they are resolved. Continuous monitoring allows the team to act quickly and stop small issues from becoming bigger problems.
RAID Analysis often leads to important decisions, such as how to handle risks or resolve issues. These decisions should be based on facts and careful analysis. Clearly document and share the reasons behind each decision so the whole team understands the chosen approach.
A RAID log is a central document that records all risks, assumptions, issues and dependencies. It includes descriptions, impact levels, owners, deadlines and current status. Keeping this log up to date improves visibility, accountability and communication throughout the project.
Creating a RAID document involves organizing information about Risks, Assumptions, Issues, and Dependencies in a clear and structured way. Here's the step-by-step approach:
1) Start by arranging a meeting with key team members and stakeholders.
2) This session allows everyone to openly discuss and identify potential Risks, Assumptions, Issues, and Dependencies.
3) Involving different perspectives helps create a more complete view of the project and encourages open communication.
1) During the meeting, work together to clearly define each RAID component.
2) Risks may relate to finances or technical challenges.
3) Assumptions could involve resources or stakeholder expectations.
4) Issues refer to current problems.
5) Dependencies highlight task relationships and sequencing.
1) Use the identified information to build a RAID log.
2) List each item under its relevant category and include clear descriptions, impact levels, priorities, owners and planned actions.
3) A well-structured log makes it easier for everyone to understand and manage each element.
1) Distribute the RAID log to the project team and stakeholders.
2) Clear visibility ensures everyone understands the challenges, their potential impact and the actions being taken.
3) This shared understanding supports collaboration and consistent decision-making.
1) Keep the RAID document up to date as the project evolves.
2) New risks may appear, assumptions may change, issues can be resolved and dependencies may shift.
3) Regular reviews help the team respond quickly to changes and manage the project proactively.
Using RAID Analysis offers clear advantages for Project Managers and their teams. Here are the key benefits:
RAID Analysis supports early identification and management of risks. When applied consistently along with stakeholder involvement, it helps uncover potential problems before they escalate. This supports the creation of effective mitigation plans and reduces both the likelihood and impact of negative events.
RAID Analysis helps ensure that the projects remain aligned with the wider organizational objectives. It highlights the potential conflicts or opportunities for better synergy, supports collaboration across teams and enables better strategic decision-making at project as well as portfolio levels.
By clearly recording the risks, assumptions, issues and dependencies, RAID Analysis enables informed, data-driven decision-making. It provides a clear view of project challenges and priorities. This allows the resources to be directed where they are most needed and enables timely adjustments to plans.
RAID improves visibility across the project by offering a clear picture of the current status, risks and challenges. Regular updates and open communication show a proactive approach to management. This goes a long way in building trust and confidence among stakeholders and encourages stronger project support.
Orchestrate time and turn timelines into project triumphs. Learn how in our PMI Scheduling Professional (PMI-SP)® Certification – Sign up today!
While RAID Analysis offers valuable structure and clarity, it's not without limitations. Here are some challenges associated with it:
For projects with limited scope or complexity, a detailed RAID Analysis may be unnecessary. In such cases, the added documentation and processes can create avoidable administrative effort, diverting resources from more critical activities.
Proper RAID Analysis requires ongoing commitment, including regular discussions, detailed documentation and continuous monitoring. For teams working with tight timelines or limited capacity, this can place additional pressure on already stretched resources.
If RAID logs are not updated consistently, they can quickly become inaccurate. This may result in decisions being made using outdated information, while new risks, issues or dependencies remain unidentified.
Relying too heavily on RAID Analysis can sometimes hinder progress. Excessive focus may lead to over-analysis, reduced responsiveness to change, or neglect of other important project factors such as team collaboration, stakeholder engagement and process improvement.
Here are the key practices to follow for effective implementation of RAID in Project Management:
1) Keep RAID Simple and Relevant: To avoid unnecessary administration, tailor the level of detail to the project size and complexity.
2) Update RAID Regularly: Review and refresh risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies throughout the project lifecycle to keep information accurate.
3) Assign Clear Ownership: Ensure every RAID item has an accountable owner responsible for monitoring and resolution.
4) Prioritize What Matters Most: Focus on high-impact, high-likelihood items rather than treating all entries equally.
5) Use RAID as a Communication Tool: Share the RAID log openly with the team and stakeholders to support transparency and alignment.
6) Link RAID to Decision-making: Actively use RAID insights when planning actions, allocating resources and managing changes.
7) Avoid Over-analysis: Use RAID to support progress, not slow it down. Balance analysis with action and flexibility.
8) Integrate RAID Into Existing Processes: Align RAID reviews with project meetings, status updates, and governance routines for consistency.
9) Continuous Learning: It's vital that you learn as much as you can from the RAID process and apply these lessons learned in future projects.
RAID in Project Management transforms uncertainty into structure, thus helping project teams stay alert and proactive. By consistently tracking the risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies, Managers gain better control. When applied thoughtfully, RAID turns complex projects into manageable journeys driven by accountability and confidence across teams, timelines, and business environments.
Shape your project leadership journey the right way. Sign up for our Project Management Institute (PMI)® Certification now!






© Copyright 2025. All rights reserved. Contact: PMP® TRAINING ACADEMY.


