









Uncertainty is unavoidable in business, but it does not have to create disorder. Every project, decision, and strategy carries risk, from budgets and timelines to technology and people. Without a clear approach, these risks can quickly slow things down and cause big problems. That's where a proper Risk Management Plan makes the difference.
It provides a clear approach to identify potential issues early, understand their impact, and respond effectively, helping organizations stay prepared and in control. In this blog, we’ll explore all about the Risk Management Plan and how to create one for your business. Let's dive in!
A Risk Management Plan is a formal document that identifies potential risks, analyzes their likelihood and impact, and outlines actions to monitor, manage, and mitigate those risks. It defines how risks are found, who is responsible for managing them, what risk levels are acceptable, and how issues should be escalated when needed.
Rather than focusing only on threats, a Risk Management Plan also considers opportunities. Some risks may lead to positive outcomes if managed well, such as adopting new technology ahead of competitors or getting into emerging markets early.
Risk Management Plans are important because they help organizations stay in control. Without a clear plan, teams often react to problems when they occur, leading to delays, higher costs, and weak decisions.
A Risk Management Plan helps businesses and organizations in the following ways:
1) Proactive Risk Identification: Helps organizations spot potential problems at an early stage to control risks before they grow into serious issues.
2) Reduces Delays and Extra Costs: By planning for risks in advance, teams can avoid last-minute fixes. This helps keep projects on schedule and prevents unexpected expenses.
3) Improves Decision-making: Clear risk information supports better decisions. Teams can weigh options carefully, understand possible outcomes, and choose the most suitable action.
4) Protects Business Resources: A Risk Management Plan helps safeguard money, people, systems, and equipment by reducing the chance of major disruptions or losses.
5) Builds Stakeholder Confidence: Clients, investors, and leaders feel confident when risks are managed properly. It shows that the organization is prepared and responsible.
6) Supports Compliance and Governance: Many industries require formal Risk Management. A structured plan helps organizations meet legal and policy requirements.
7) Encourages Preventive Problem-solving: Instead of reacting to issues, teams can take preventive action. This leads to smoother operations and stronger overall performance.
A Risk Management Plan is created through a structured approach. Each step builds on the previous one to ensure risks are identified, assessed, and managed correctly. Below are the key steps:
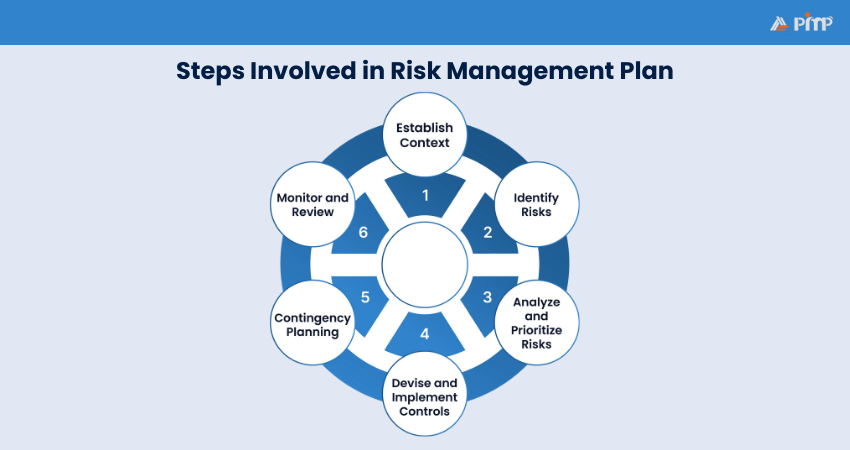
Establishing context sets the foundation for the entire plan. At this stage, organizations look at their goals, project scope, internal resources, and external factors such as laws, market conditions, and stakeholders’ expectations. This helps ensure that risks are viewed in the right context.
It is also important to define how much risk the organization is willing to accept. Knowing this helps guide later decisions.
Risk identification means finding anything that could affect business goals and objectives. These risks can come from many areas, such as operations, finances, technology, legal issues, or reputational risks. Each risk needs to be described clearly, so everyone understands what could happen and the reasons behind it.
Common ways to identify risks include team discussions, expert interviews, reviewing past projects, and analyzing data.
After identifying risks, the next step is to analyze them. This means looking at how likely each risk is and how serious the impact would be if it happened. Many people use simple rating systems such as a risk assessment matrix to prioritize the risks. The ratings of low, medium, and high help teams see which risks need the most attention.
The purpose of this step is to focus on the most important risks. Not every risk needs the same level of action, so prioritizing helps use time and resources wisely.
Controls are the actions taken to manage identified risks. These risk control measures can be preventative, detective, or corrective in nature. Common strategies include avoiding the risk altogether, reducing its impact, transferring it through insurance or contracts, or accepting it with clear justification.
Each risk control measure has a person who is responsible for implementing and monitoring it once it is in action. Controls should be practical and not overly complex.
Contingency planning is basically like a backup plan and in the Risk Management Plan, it prepares teams for situations when risk happens despite strong control measures. This plan explains the necessary steps to take for the issue, who to contact, and how to respond quickly. This helps avoid confusion and delays during critical moments.
Good contingency plans also include early warning signs. This allows teams to act early before a problem becomes serious.
Explore essential Project Management knowledge with the PMI Project Management Ready® Certification – Register today!
Risk Management is not a static process. Instead, it is dynamic and evolving since risks change over time as conditions evolve, objectives shift, and new information emerges. To address this, you can conduct a regular review and continuous monitoring to check if the control actions are relevant to the issue that you are facing.
This step also encourages continuous improvement. You will keep monitoring and stay updated when there are changes required.
Understanding What is a Risk Management Plan helps you know that it is valuable in many situations of a project. Here are the instances where you can use it:
1) During Project Initiation: Creating a Risk Management Plan at the start of a project helps identify potential risks early. It allows teams to set controls, assign responsibilities, and plan responses before work begins.
2) During Large or Complex Projects: These plans are essential for projects with many tasks, teams, or dependencies. They help manage uncertainties related to timelines, costs, and resources.
3) During Business Changes: Major changes such as process improvements, restructuring, or digital transformation carry risks. A proper plan helps reduce disruption and supports smoother transitions.
4) New Product or Service Launches: Launching something new involves market, technical, and operational risks. Planning ahead helps address potential issues before they affect customers.
5) During Compliance Activities: Industries with strict regulations require structured Risk Management. A Risk Management Plan helps ensure compliance and avoid legal penalties.
6) High-risk Operational Environments: Organizations operating in areas like construction, digital security, or healthcare benefit from risk planning to reduce safety, operational, and system risks.
7) Working With External Partners: Collaborating with vendors, contractors, or third parties introduces dependency risks. A Risk Management Plan helps manage shared responsibilities and expectations.
8) During Strategic Business Decision-making: Major investments or strategic decisions involve uncertainty. A Risk Management Plan supports informed decision-making and reduces unexpected outcomes.
Prepare to oversee complex programs with Program Management Professional (PgMP)® Certification – Join now!
A well-structured Risk Management Plan includes several connected components that work together to identify, assess, and manage risks effectively. Key components include:
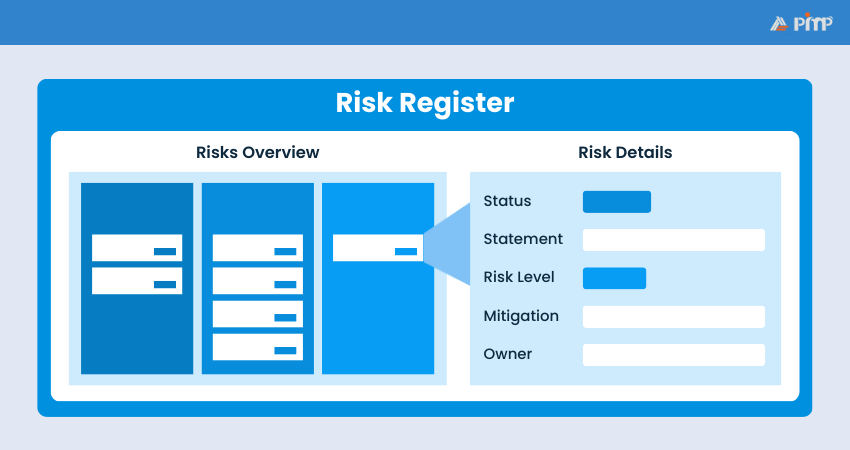
A risk register is a single place where all risks are listed. It includes what the risk is, how serious it could be, how likely it is to happen, who is responsible for it, and its current status. This helps teams keep track of risks and make informed decisions.
A risk assessment matrix is a simple chart that shows how often a risk may occur and how much impact it could have. It helps teams decide which risks need urgent attention and which ones can be monitored.
These are the actions taken to reduce risks. This includes improving processes, using security tools, updating policies, or providing training. Clear actions help reduce the chance of problems occurring.
This component explains who is responsible for managing risks. It shows who will identify risks, decide actions, and keep track of them. Clear responsibilities help avoid confusion and ensure risks are handled on time.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics help measure how effective Risk Management efforts are. Tracking these indicators helps organizations improve their risk mitigation practices over time.
To understand how a Risk Management Plan works in practice, let’s consider a project involving the construction of a new office building. Such projects face various risks related to cost, time, safety, and approvals.
Possible risks include delays in material delivery, bad weather, safety incidents on-site, rising costs, and delays in regulatory approvals.
Each identified risk is checked based on the chance of it happening and how serious the impact would be. This helps the team decide which risks need immediate action and which can be monitored.
For example, delays in material supply may have a medium chance of occurring but a high impact on the project schedule. To reduce this risk, the team may use multiple suppliers and maintain backup stock.
If material delays still occur, a contingency plan is followed. This may involve modifying the project timeline or reallocating workers to other tasks to minimize disruption.
This example shows how early risk identification, clear controls, and prepared responses help projects stay on track, reduce disruption, and improve overall project performance.
Enhance your ability to plan and control project schedules with PMI Scheduling Professional (PMI-SP)® Certification – Sign up soon!
Now, let’s go through the best practices that you can follow while drafting a Risk Management Plan:
1) Align With Business Goals: Risk Management should support what the business or project is trying to achieve. Risks should be reviewed based on how they affect key goals.
2) Identify Risks Early: Start looking for risks at the beginning and keep checking them as work continues. This helps catch new risks and keep plans up to date.
3) Give Clear Responsibility: Each risk should be assigned to someone. This makes sure risks are not ignored, and actions are taken on time.
4) Keep the Plan Simple: The plan should be easy to understand and follow. Focus on practical actions instead of making it too complicated.
5) Share Risk Information Clearly: Make sure the right people know about important risks. Clear sharing helps teams act quickly when needed.
6) Review and Improve: Check how risks are managed and learn from past problems. This helps improve your Risk Management approach.
A Risk Management Plan helps organizations stay prepared in uncertain business situations. By identifying risks early, assessing their impact, and planning clear actions, teams can avoid delays, reduce costs, and make better decisions. A well-structured plan not only protects business goals but also builds confidence, stability, and long-term success.
Equip with core Project Management skills through Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) ® Training – Begin your journey now!






© Copyright 2025. All rights reserved. Contact: PMP® TRAINING ACADEMY.


