









Successful projects are never built on guesswork. They rely on clear structure, well-defined outcomes and organized effort. A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) brings order to any level of complexity by breaking a project into manageable pieces. It transforms big goals into clear deliverables, timelines, and responsibilities.
In Project Management, WBS essentially acts as the foundation for planning, budgeting, and control. This blog explores what a Work Breakdown Structure is and how it dissects a complex project into bite-sized, manageable pieces, making the impossible feel achievable. So read on and master this backbone of successful Project Management!
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a structured approach in Project Management that divides a project into smaller, manageable components. It organizes the entire scope of work into clear deliverables and tasks, making planning more accurate and execution more controlled.
By defining what needs to be done, a WBS helps teams estimate time and costs, assign responsibilities, identify dependencies, and monitor progress. It improves visibility across the project, reduces the risk of missed work, and supports better communication among stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle.
A Work Breakdown Structure consists of several essential elements for defining and organizing project work properly. These include:
1) Deliverable: It's a measurable output, tangible or intangible, created through the project and provided to an internal or external customer.
2) Control Account: This is a WBS element assigned to a specific organizational unit, used to track costs, progress and performance.
3) Planning Package: This is a grouping of related tasks used for future planning when detailed activities are not yet fully defined.
4) Work Package: This is the lowest level of the WBS that combines related activities that can be scheduled, monitored and controlled.
5) WBS Dictionary: This is a reference document that contains detailed descriptions and key information for every WBS element.
Here are the different types of Work Breakdown Structures that help you define deliverables and schedule tasks:
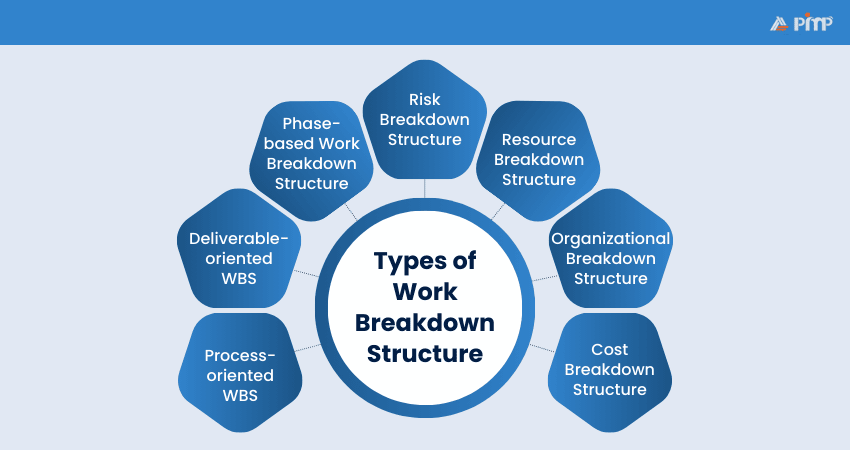
A Process-oriented WBS organizes the project based on the activities or processes required to complete the work. Tasks are grouped by actions such as design, development, testing, and deployment. This approach is useful when the workflow matters more than the final deliverables.
A Deliverable-oriented WBS structures the project around outputs and results rather than activities. Each section represents a specific deliverable such as a report, system, or product feature. This type improves clarity on what must be produced and helps manage scope effectively.
This type divides the project according to project phases, such as initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure. It is useful for tracking progress across each stage of the project lifecycle and supports better governance and control.
A Risk Breakdown Structure categorises potential project risks into structured levels. Risks may be grouped under technical, financial, operational, or external categories. This helps teams identify threats early and manage risk more systematically.
Wield the ultimate power move in your Project Management career by signing up for the Project Management Institute (PMI)® Certification today!
This structure organizes project work based on the resources involved, such as people, tools, equipment, or materials. It helps with capacity planning, workload distribution, and understanding how resources are allocated across the project.
An Organizational Breakdown Structure groups work according to departments, teams, or business units. It clarifies accountability by showing which part of the organization is responsible for each area of work.
A Cost Breakdown Structure organizes the project according to budget categories and cost elements. It helps track spending, monitor financial performance, and improve cost control throughout the project lifecycle.
To develop an effective Work Breakdown Structure, follow these steps:
Establish the Project Scope: Clearly define the overall objective, key deliverables, constraints, timelines and boundaries.
1) Collect Essential Project Documents: Compile the important references such as the Project Management plan, risk register and scope statement.
2) Build a Hierarchical Framework: Arrange the project into a layered structure, placing major deliverables at the top and supporting elements beneath them.
3) Break Down Deliverables: Divide each high-level deliverable into smaller, manageable tasks or work packages that can be planned, assigned and monitored.
4) Assign Responsibility: Identify the individual or team accountable for each task to ensure ownership, coordination and clear communication.
5) Develop the WBS Dictionary: Document detailed information for every WBS element, including required resources, estimated time, and task relationships. This can be presented as an outline or diagram showing connections between work packages.
6) Create the Project Schedule: Once the WBS is reviewed and approved, convert it into a Gantt chart. This schedule becomes a key tool for tracking progress.
A Work Breakdown Structure plays a critical role across the entire project lifecycle. Below are key benefits that demonstrate why a WBS is essential for Project Managers:
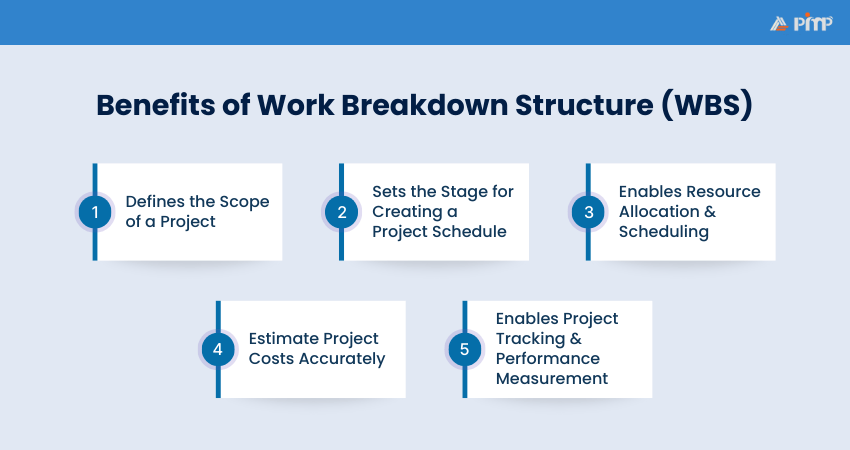
A WBS outlines exactly what the project will deliver by breaking outcomes into manageable components. This clarity reduces ambiguity, prevents scope creep and aligns stakeholders on what is included and excluded.
By identifying and organizing all the key tasks, a WBS provides the basis for sequencing activities, setting milestones and estimating durations. This structured approach enables realistic timelines.
A WBS helps identify the people, equipment and materials needed for each task. This enables balanced workloads and avoids overuse or shortages of resources.
Breaking work into smaller components allows the costs to be estimated at a detailed level. This supports bottom-up budgeting, improves financial accuracy and boosts cost control.
Once established, the WBS becomes a benchmark for monitoring progress, costs and timelines. It allows Managers to spot variances early, take corrective action and maintain accountability.
Looking for some professional guidance on flawless project scheduling? Our PMI Scheduling Professional (PMI-SP)® Certification will help you out - Sign up now!
The following best practices will help make your WBS more effective, manageable and aligned with project goals and reporting needs:
Make sure the WBS covers 100% of the project work defined in the scope so nothing is neglected. Focus on deliverables and results rather than actions or tasks to avoid confusion.
Make sure the tasks are mutually exclusive with no overlap, thus keeping elements distinct. Keep the structure simple and clear by avoiding too many hierarchical levels that can complicate understanding.
Use the 8/80 rule. Each work package should take at least 8 hours but no more than 80 hours to complete. If a package falls outside this range, consider breaking it down further or combining it with related work.
Try to restrict work packages so they fit within a single reporting period (weekly or monthly). If a package spans multiple periods, break it into smaller elements to improve tracking and reporting.
A Work Breakdown Structure serves multiple purposes throughout a project. Here's how you can use it:
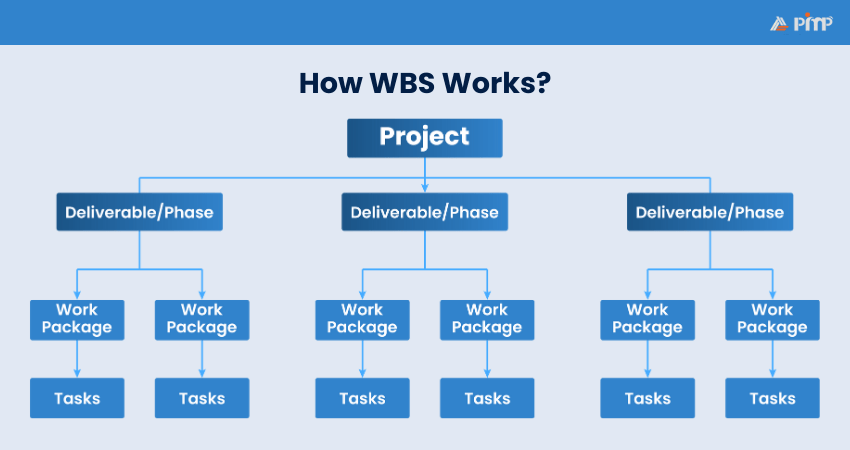
Work packages represent the smallest manageable units of work that can be planned, scheduled, costed and tracked independently. They combine related tasks into a single, measurable, deliverable, and are assigned to a specific team or individual.
For example, in a website development project, “Design Homepage Layout” can be a work package assigned to the design team with a defined duration, cost and quality standard.
Planning packages sit between control accounts and work packages and are used when future work is identified but not yet detailed. They allow Project Managers to allocate budget and outline scope early on.
For example, “Future Mobile App Enhancements” may be defined as a planning package when requirements are still being finalized, with detailed tasks added once designs are approved.
Control accounts act as key management checkpoints where scope, schedule, and cost are brought together for monitoring and reporting. They usually include several work packages and, in some cases, planning packages.
For example, “Website Development Phase” can be a control account that groups work packages such as frontend design, backend development, and testing. This allows Managers to track overall progress and costs against the plan.
A Work Breakdown Structure turns complex projects into clear, achievable actions. By organizing the scope into structured deliverables, it boosts the planning process and improves control over it. It remains one of the most powerful tools for delivering projects on time, within budget and with clarity from start to finish.
Shape the future of your organization with Portfolio Management Professional (PfMP)® Certification - Sign up now!






© Copyright 2025. All rights reserved. Contact: PMP® TRAINING ACADEMY.


