







 10 Sep 2024
10 Sep 2024


Behind every on‑time, on‑budget project lies a well‑crafted Project Schedule. It’s more than a list of tasks; it’s a structured timeline that connects the goals, resources and deadlines into a clear plan of action. A strong Project Schedule keeps teams aligned and helps anticipate risks before they impact progress.
In this blog, we explore what is a Project Schedule, break down its core components, explain some popular scheduling techniques and share practical examples that bring such planning to life. So read on and turn your most complex project plan into action with ease.
A Project Schedule is a structured plan that defines when project tasks will start and finish, how they relate to one another, and who is responsible for completing them. It brings all essential timelines, activities, and dependencies into a single view, making progress easy to track in real time. This clarity helps teams coordinate work, identify risks early, and maintain control throughout the project lifecycle.
A Project Schedule keeps the project moving in the right direction. It shows how tasks are connected, helps teams stay aligned, and supports effective management of time, cost, and scope. With a clear schedule in place, teams can reduce the risk of delays, budget overruns, and uncontrolled scope changes.
When changes occur, a well-structured schedule makes it easier to adjust plans without disrupting the entire project. This is why using a Project Schedule is essential:
1) Clarity: Provides clear visibility into tasks, timelines, and deadlines.
2) Direction: Establishes a clear goal with a structured path to achieve it.
3) Triple Constraint Control: Balances time, cost, and scope to maintain project stability.
4) Time Management: Uses logical task sequencing and deadlines to keep progress on track.
5) Risk Management: Identifies potential bottlenecks and issues early.
6) Live Progress Tracking: Compares planned versus actual progress to show whether the project is ahead, on track, or behind schedule.
A Project Schedule is built from several core elements that help structure work and keep the project progressing smoothly. Here are the components: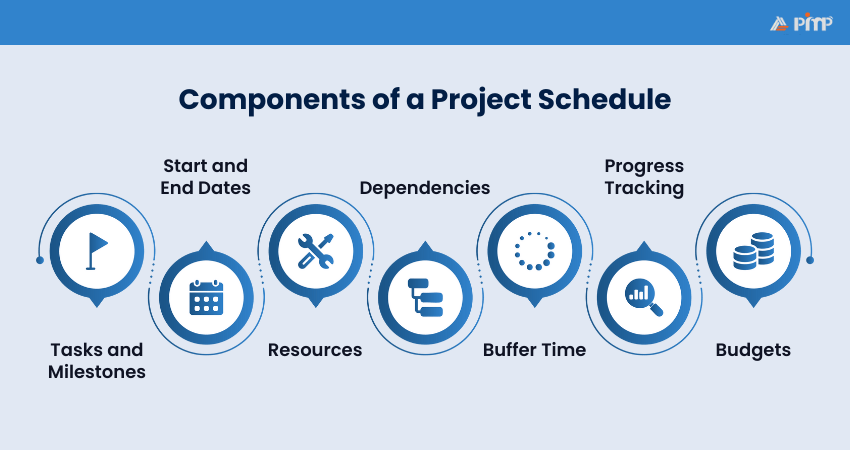
1) Tasks and Milestones: Every project consists of individual tasks, ranging from small activities to major pieces of work. Milestones represent significant checkpoints that signal the completion of key phases and highlight progress.
2) Start and End Dates: Each task is assigned clear start and finish dates, defining its timeframe and preventing work from drifting. This gives teams a shared understanding of priorities and expected duration.
3) Resources: Resources include the people, tools, and materials required to complete each task. The schedule clarifies responsibilities and ensures everyone knows what they are accountable for.
4) Dependencies: Certain tasks rely on others being completed first. Mapping these dependencies shows the correct order of work and helps avoid delays caused by starting tasks too early.
5) Buffer Time: Unplanned issues are inevitable. Buffer time builds flexibility into the schedule. This allows teams to absorb delays without derailing the entire project.
6) Progress Tracking: A Project Schedule supports ongoing monitoring, not just planning. Regular updates on task status help identify issues early and enable timely adjustments.
7) Budgets: When tasks are sequenced, Financial Management becomes easier. Linking budget information to the schedule allows teams to track spending against the baseline.
Looking to set the benchmark for project excellence? Our PMP® Certification will show you the way - Sign up now!
Start by clearly understanding the project’s goals. Working together as a team helps capture all tasks and make realistic estimates. You can build your Project Schedule using the steps below: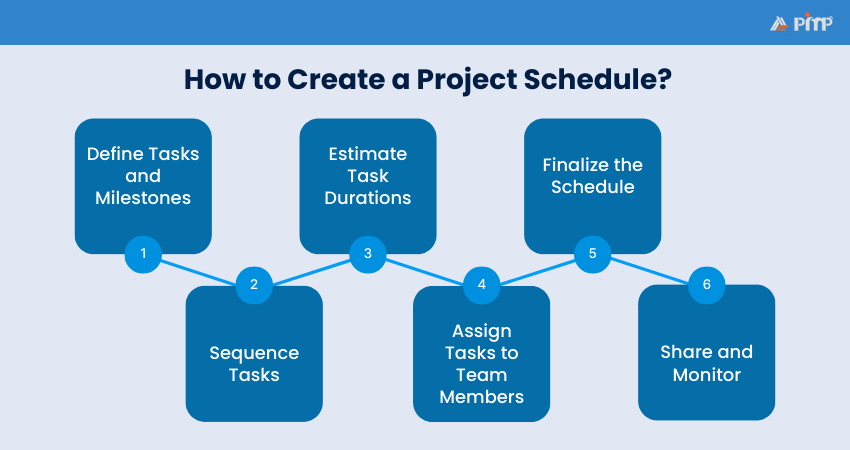
Break large pieces of work into smaller, manageable tasks that are easier to estimate. Identify which tasks depend on others and group related tasks into milestones. These can always be adjusted later if plans change.
Decide the order in which the tasks must be completed, keeping dependencies in mind. Project Scheduling tools can help you visualize how workflows from start to finish. Some teams find it useful to work backwards from the end goal.
Smaller tasks are easier to estimate accurately. Work as a team to agree on realistic timelines, using past experience to avoid over- or under-estimating how long tasks will take
Allocate tasks based on skills and availability. Balance the workload so no one is overloaded, and identify tasks that can run in parallel rather than one after another.
Before starting work, share the schedule with the project sponsor for review. If timelines are tight, you may need to adjust the scope or split the project into phases to meet business needs.
Once approved, share the schedule with all stakeholders so everyone understands the timeline. Monitor progress regularly using project tools, flag issues early and update the schedule as needed to keep the project on track.
When implemented effectively, a Project Schedule offers a clear overview of the project, reduces uncertainty and makes day-to-day work easier to manage. Once your schedule is ready, follow these steps to put it into action:
Distribute the Project Schedule to everyone involved so that the responsibilities and timelines are clear. Invite team members to share their feedback or concerns about their assigned tasks. Keep the responses organized by using a central feedback location and setting a clear deadline.
After reviewing input, update the schedule and share the final version with all stakeholders. Make sure that the related documents, such as the project brief and executive summary, reflect the agreed schedule.
Change is inevitable during any project. So regularly review the schedule and be prepared to update it when unexpected issues arise. A clear Change Management approach allows you to adapt without disrupting progress. Managing the schedule centrally ensures that everyone is working from the latest version and avoids confusion.
Once proven, turn your Project Schedule into a template to save time on future work. For recurring projects, such as annual events or repeat initiatives, a reusable schedule allows teams to launch new projects faster by building on what already works.
Build the strongest Project Management foundation with our Certified Associate in Project Management (CAPM) ® Training - Register now!
Different Project Scheduling techniques suit different project types, and choosing the right one can significantly improve planning and execution. Here are some proven techniques to try:
Task lists are best for smaller projects with minimal dependencies. They clearly outline tasks and assign responsibilities, though they can become a headache to manage as complexity increases.
Example: For a small office move, tasks such as packing equipment, booking movers and setting up workstations can be listed and assigned. This makes responsibilities clear and progress easy to track.
Calendars show tasks across a timeline, helping teams spot overlaps and manage deadlines. However, they do not clearly show task ownership or dependencies.
Example: When planning a quarterly webinar series, a calendar helps schedule session dates and avoid clashes, while making sure there’s enough preparation time between events.
Gantt charts visually display tasks, durations, dependencies, and overlaps, giving a complete view of the project timeline.
Example: In a Software Development project, a Gantt chart can map design, development, testing, and deployment phases. This shows which tasks must finish before others begin.
PERT estimates task durations using optimistic, pessimistic and most likely timelines, making it suitable for projects with uncertainty or greater complexity.
Example: When organizing a large technology conference, PERT helps manage uncertainties such as speaker confirmations and sponsorship approvals by identifying the critical path and potential delays.
CPM detects the sequence of tasks that directly impact the project’s completion date. Any delay in these tasks will delay the entire project.
Example: In a construction project, tasks like foundation work, structural framing, and electrical installation form the critical path. This means delays in any of these activities will affect the overall completion timeline.
Agile scheduling focuses on short, iterative work cycles known as sprints, allowing teams to deliver value frequently and adapt to feedback.
Example: For a Mobile App launch, the team may use two-week sprints to release features such as login, user profiles and notifications. They can adjust priorities based on user feedback after each sprint.
This approach assigns tasks based on available people, tools, and equipment, ensuring workloads are balanced and resources are not overused.
Example: In a marketing campaign, resource-oriented scheduling helps distribute tasks like content creation, design and social media management evenly across the team to avoid overloading any single role.
Creating a schedule that genuinely supports your project objectives is key to good Project Management. The following best practices can help ensure that your schedule remains practical and flexible:
1) Define Clear Milestones: Establish well-defined milestones to track progress and keep the team focused on each stage of the project.
2) Set Realistic Timelines: Allow sufficient time for tasks and include buffers for unexpected delays to make deadlines more achievable.
3) Prioritize Task Dependencies: Identify and map task dependencies to prevent bottlenecks and maintain a smooth flow of work.
4) Allocate Resources Effectively: Assign tasks based on team availability and expertise to ensure each phase is properly supported.
5) Monitor and Adjust Regularly: Review the schedule often to gauge progress and make timely adjustments as circumstances change.
Validate your ability to manage multiple complex project initiatives with our Program Management Professional (PgMP)® Certification - Sign up now!
The following three examples will enhance your understanding of crafting a Project Schedule:
Overview: Plan all the stages needed to launch a new product on time.
Schedule Elements:
1) Market research and concept validation
2) Product Design, development and internal checks
3) Marketing prep (content, creatives, campaigns)
4) Pre-launch promotion
5) Post-launch monitoring and review
Outcome: A clear timeline ensures teams know what tasks must finish first and keeps launch milestones visible to everyone.

Overview: Used for organizing events such as conferences, workshops or annual meetings.
Schedule Elements:
1) Confirm venue and logistics
2) Book speakers and sponsors
3) Open registration and promote event
4) Final walk-through and run-through rehearsals
5) Event day execution and post-event follow-up
Outcome: A timeline that maps each stage to specific dates helps prevent last-minute rushes and missed tasks.
Overview: Schedule the redesign of a company website, from planning to launch.
Schedule Elements:
1) Project kickoff and requirements gathering
2) Wireframe and UI design
3) Development and coding
4) Testing and bug fixes
5) Launch and post-launch analytics
Outcome: Breaking the project into phases with deadlines keeps design, development, and QA in sync and reduces rework.
A good Project Schedule is more than dates on a timeline. It brings unparalleled control to complex work. By combining the right components, techniques and real-world examples, teams can plan smarter and adapt faster. When used well, it becomes the backbone of successful project execution, keeping goals visible and progress moving forward.
Power up your career with our Project Management Institute (PMI)® Certification where global standards meet real‑world leadership. Sign up now!






© Copyright 2025. All rights reserved. Contact: PMP® TRAINING ACADEMY.


